Page 284 - Semiconductor Manufacturing Handbook
P. 284
Geng(SMH)_CH19.qxd 04/04/2005 20:00 Page 19.11
INSPECTION, MEASUREMENT, AND TEST
INSPECTION, MEASUREMENT, AND TEST 19.11
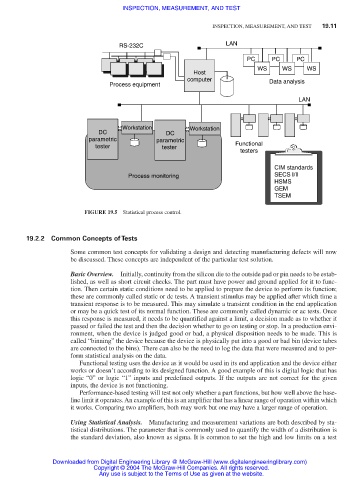
RS-232C LAN
PC PC PC
WS WS WS
Host
computer Data analysis
Process equipment
LAN
Workstation Workstation
DC DC
parametric parametric
tester tester Functional
testers
CIM standards
Process monitoring SECS I/II
HSMS
GEM
TSEM
FIGURE 19.5 Statistical process control.
19.2.2 Common Concepts of Tests
Some common test concepts for validating a design and detecting manufacturing defects will now
be discussed. These concepts are independent of the particular test solution.
Basic Overview. Initially, continuity from the silicon die to the outside pad or pin needs to be estab-
lished, as well as short circuit checks. The part must have power and ground applied for it to func-
tion. Then certain static conditions need to be applied to prepare the device to perform its function;
these are commonly called static or dc tests. A transient stimulus may be applied after which time a
transient response is to be measured. This may simulate a transient condition in the end application
or may be a quick test of its normal function. These are commonly called dynamic or ac tests. Once
this response is measured, it needs to be quantified against a limit, a decision made as to whether it
passed or failed the test and then the decision whether to go on testing or stop. In a production envi-
ronment, when the device is judged good or bad, a physical disposition needs to be made. This is
called “binning” the device because the device is physically put into a good or bad bin (device tubes
are connected to the bins). There can also be the need to log the data that were measured and to per-
form statistical analysis on the data.
Functional testing uses the device as it would be used in its end application and the device either
works or doesn’t according to its designed function. A good example of this is digital logic that has
logic “0” or logic “1” inputs and predefined outputs. If the outputs are not correct for the given
inputs, the device is not functioning.
Performance-based testing will test not only whether a part functions, but how well above the base-
line limit it operates. An example of this is an amplifier that has a linear range of operation within which
it works. Comparing two amplifiers, both may work but one may have a larger range of operation.
Using Statistical Analysis. Manufacturing and measurement variations are both described by sta-
tistical distributions. The parameter that is commonly used to quantify the width of a distribution is
the standard deviation, also known as sigma. It is common to set the high and low limits on a test
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.