Page 225 - Separation process engineering
P. 225
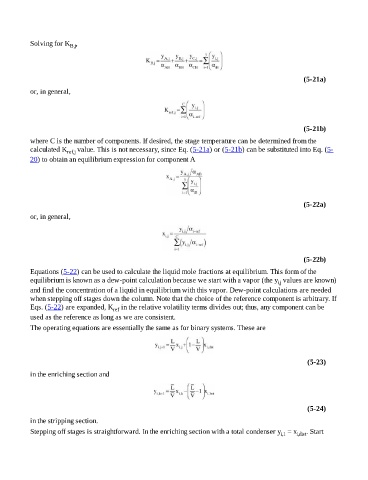
Solving for K ,
B,j
(5-21a)
or, in general,
(5-21b)
where C is the number of components. If desired, the stage temperature can be determined from the
calculated K ref,j value. This is not necessary, since Eq. (5-21a) or (5-21b) can be substituted into Eq. (5-
20) to obtain an equilibrium expression for component A
(5-22a)
or, in general,
(5-22b)
Equations (5-22) can be used to calculate the liquid mole fractions at equilibrium. This form of the
equilibrium is known as a dew-point calculation because we start with a vapor (the y values are known)
i,j
and find the concentration of a liquid in equilibrium with this vapor. Dew-point calculations are needed
when stepping off stages down the column. Note that the choice of the reference component is arbitrary. If
Eqs. (5-22) are expanded, K in the relative volatility terms divides out; thus, any component can be
ref
used as the reference as long as we are consistent.
The operating equations are essentially the same as for binary systems. These are
(5-23)
in the enriching section and
(5-24)
in the stripping section.
Stepping off stages is straightforward. In the enriching section with a total condenser y = x i,dist . Start
i,1