Page 162 - Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design
P. 162
bud29281_ch03_071-146.qxd 11/25/09 4:55PM Page 137 ntt 203:MHDQ196:bud29281:0073529281:bud29281_pagefiles:
Load and Stress Analysis 137
y
d A d B d A d C
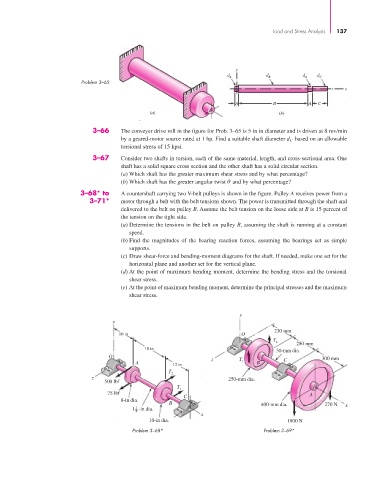
Problem 3–65
x
A B A C
(a) (b)
3–66 The conveyer drive roll in the figure for Prob. 3–65 is 5 in in diameter and is driven at 8 rev/min
by a geared-motor source rated at 1 hp. Find a suitable shaft diameter d C based on an allowable
torsional stress of 15 kpsi.
3–67 Consider two shafts in torsion, each of the same material, length, and cross-sectional area. One
shaft has a solid square cross section and the other shaft has a solid circular section.
(a) Which shaft has the greater maximum shear stress and by what percentage?
(b) Which shaft has the greater angular twist θ and by what percentage?
3–68* to A countershaft carrying two V-belt pulleys is shown in the figure. Pulley A receives power from a
3–71* motor through a belt with the belt tensions shown. The power is transmitted through the shaft and
delivered to the belt on pulley B. Assume the belt tension on the loose side at B is 15 percent of
the tension on the tight side.
(a) Determine the tensions in the belt on pulley B, assuming the shaft is running at a constant
speed.
(b) Find the magnitudes of the bearing reaction forces, assuming the bearings act as simple
supports.
(c) Draw shear-force and bending-moment diagrams for the shaft. If needed, make one set for the
horizontal plane and another set for the vertical plane.
(d) At the point of maximum bending moment, determine the bending stress and the torsional
shear stress.
(e) At the point of maximum bending moment, determine the principal stresses and the maximum
shear stress.
y
y
230 mm
10 in O
T 2
280 mm
18 in 30-mm dia.
O z T 300 mm
A 1 B C
12 in
T
2
z 250-mm dia.
500 lbf
T
1
75 lbf C A
8-in dia.
B 400-mm dia. 270 N x
1
1 -in dia.
4
x
10-in dia. 1800 N
Problem 3–68* Problem 3–69*