Page 430 - Shigley's Mechanical Engineering Design
P. 430
bud29281_ch07_358-408.qxd 12/8/09 12:52PM Page 405 ntt 203:MHDQ196:bud29281:0073529281:bud29281_pagefiles:
Shafts and Shaft Components 405
steel. At steady-state speed, the gear transmits a radial load of 230 lbf and a tangential load of
633 lbf at a pitch diameter of 8 in.
(a) Determine fatigue factors of safety at any potentially critical locations.
(b) Check that deflections satisfy the suggested minimums for bearings and gears.
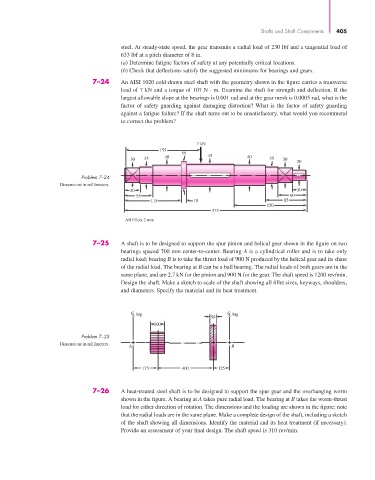
7–24 An AISI 1020 cold-drawn steel shaft with the geometry shown in the figure carries a transverse
load of 7 kN and a torque of 107 N · m. Examine the shaft for strength and deflection. If the
largest allowable slope at the bearings is 0.001 rad and at the gear mesh is 0.0005 rad, what is the
factor of safety guarding against damaging distortion? What is the factor of safety guarding
against a fatigue failure? If the shaft turns out to be unsatisfactory, what would you recommend
to correct the problem?
7 kN
155
55
40 45 40
30 35 35 30
20
Problem 7–24
Dimensions in millimeters.
30 30
55 60
115 10 85
150
375
All fillets 2 mm
7–25 A shaft is to be designed to support the spur pinion and helical gear shown in the figure on two
bearings spaced 700 mm center-to-center. Bearing A is a cylindrical roller and is to take only
radial load; bearing B is to take the thrust load of 900 N produced by the helical gear and its share
of the radial load. The bearing at B can be a ball bearing. The radial loads of both gears are in the
same plane, and are 2.7 kN for the pinion and 900 N for the gear. The shaft speed is 1200 rev/min.
Design the shaft. Make a sketch to scale of the shaft showing all fillet sizes, keyways, shoulders,
and diameters. Specify the material and its heat treatment.
C brg C brg
L
L
50
100
Problem 7–25
Dimensions in millimeters.
A B
175 400 125
7–26 A heat-treated steel shaft is to be designed to support the spur gear and the overhanging worm
shown in the figure. A bearing at A takes pure radial load. The bearing at B takes the worm-thrust
load for either direction of rotation. The dimensions and the loading are shown in the figure; note
that the radial loads are in the same plane. Make a complete design of the shaft, including a sketch
of the shaft showing all dimensions. Identify the material and its heat treatment (if necessary).
Provide an assessment of your final design. The shaft speed is 310 rev/min.