Page 192 - Steam Turbines Design, Applications, and Rerating
P. 192
Rotor Dynamics Technology 171
of three major developments. The first was the advent of high-speed,
high-capacity computers, which made it practical to perform the theo-
retical analyses of bearings without the need for many simplifying
assumptions that were required previously. The second was the avail-
ability of new instrumentation, which made it possible to obtain accu-
rate measurements of vibration amplitudes and phase angles. The
noncontacting vibration probe and the tracking filter were significant
component developments.
The third major development, which was essential to the evolution of
rotor dynamics technology, was the establishment of laboratory bear-
ing test facilities to make dynamic measurements of the journal orbit
motion while running in different types of full-size bearings.
Correlations were obtained between calculated and experimentally
observed bearing-induced rotor behavior. As a result of these develop-
ments, a new design philosophy emerged in which bearings were con-
sidered as more than just hydraulic supports for the rotor. The dynamic
characteristics of the bearings were matched to specific rotor charac-
teristics to evaluate their effect on the vibration response of the rotor-
bearing system. For example, tilting-pad bearings were originally
selected because of half-frequency, oil-whip problems. Their use was
limited to high-speed, light-load applications. Currently, tilting-pad
bearings are being applied to all rotors regardless of speed or load
because of their stiffness and damping characteristics as they affect
synchronous rotor response.
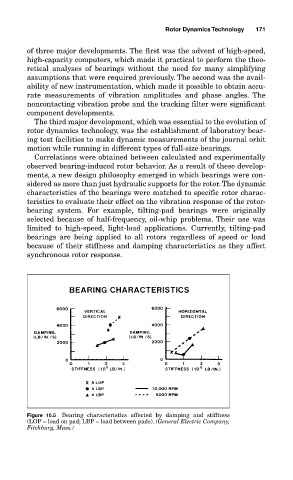
Figure 10.5 Bearing characteristics affected by damping and stiffness
(LOP = load on pad; LBP = load between pads). (General Electric Company,
Fitchburg, Mass.)