Page 157 - Sustainability in the Process Industry Integration and Optimization
P. 157
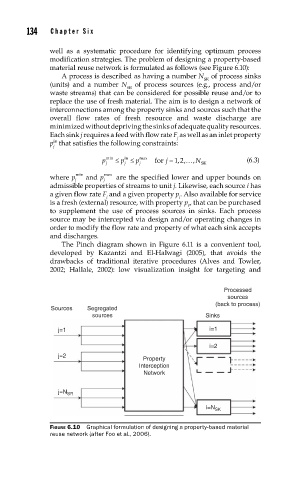
134 Cha p te r S i x
well as a systematic procedure for identifying optimum process
modification strategies. The problem of designing a property-based
material reuse network is formulated as follows (see Figure 6.10):
A process is described as having a number N of process sinks
SK
(units) and a number N of process sources (e.g., process and/or
SR
waste streams) that can be considered for possible reuse and/or to
replace the use of fresh material. The aim is to design a network of
interconnections among the property sinks and sources such that the
overall flow rates of fresh resource and waste discharge are
minimized without depriving the sinks of adequate quality resources.
Each sink j requires a feed with flow rate F as well as an inlet property
j
in
p that satisfies the following constraints:
j
p min d p d in p max for j 1,2,! ,N (6.3)
j j j SK
where p min and p max are the specified lower and upper bounds on
j j
admissible properties of streams to unit j. Likewise, each source i has
a given flow rate F and a given property p . Also available for service
i i
is a fresh (external) resource, with property p , that can be purchased
F
to supplement the use of process sources in sinks. Each process
source may be intercepted via design and/or operating changes in
order to modify the flow rate and property of what each sink accepts
and discharges.
The Pinch diagram shown in Figure 6.11 is a convenient tool,
developed by Kazantzi and El-Halwagi (2005), that avoids the
drawbacks of traditional iterative procedures (Alves and Towler,
2002; Hallale, 2002): low visualization insight for targeting and
Processed
sources
(back to process)
Sources Segregated
sources Sinks
j=1 i=1
i=2
j=2
Property
Interception
Network
j=N SR
i=N SK
FIGURE 6.10 Graphical formulation of designing a property-based material
reuse network (after Foo et al., 2006).