Page 282 - The Engineering Guide to LEED-New Construction Sustainable Construction for Engineers
P. 282
LEED Indoor Envir onmental Quality 245
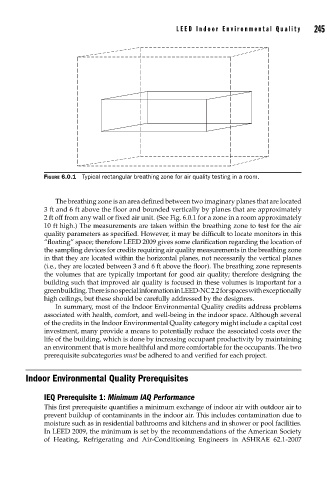
FIGURE 6.0.1 Typical rectangular breathing zone for air quality testing in a room.
The breathing zone is an area defined between two imaginary planes that are located
3 ft and 6 ft above the floor and bounded vertically by planes that are approximately
2 ft off from any wall or fixed air unit. (See Fig. 6.0.1 for a zone in a room approximately
10 ft high.) The measurements are taken within the breathing zone to test for the air
quality parameters as specified. However, it may be difficult to locate monitors in this
“floating” space; therefore LEED 2009 gives some clarification regarding the location of
the sampling devices for credits requiring air quality measurements in the breathing zone
in that they are located within the horizontal planes, not necessarily the vertical planes
(i.e., they are located between 3 and 6 ft above the floor). The breathing zone represents
the volumes that are typically important for good air quality; therefore designing the
building such that improved air quality is focused in these volumes is important for a
green building. There is no special information in LEED-NC 2.2 for spaces with exceptionally
high ceilings, but these should be carefully addressed by the designers.
In summary, most of the Indoor Environmental Quality credits address problems
associated with health, comfort, and well-being in the indoor space. Although several
of the credits in the Indoor Environmental Quality category might include a capital cost
investment, many provide a means to potentially reduce the associated costs over the
life of the building, which is done by increasing occupant productivity by maintaining
an environment that is more healthful and more comfortable for the occupants. The two
prerequisite subcategories must be adhered to and verified for each project.
Indoor Environmental Quality Prerequisites
IEQ Prerequisite 1: Minimum IAQ Performance
This first prerequisite quantifies a minimum exchange of indoor air with outdoor air to
prevent buildup of contaminants in the indoor air. This includes contamination due to
moisture such as in residential bathrooms and kitchens and in shower or pool facilities.
In LEED 2009, the minimum is set by the recommendations of the American Society
of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers in ASHRAE 62.1-2007