Page 80 - The Geological Interpretation of Well Logs
P. 80
~ THE GEOLOGICAL INTERPRETATION OP WELL LOGS -
Table 7.3 Typical modern gamma ray tools. they cause a flash. These are collected by the photo-mul-
tiplier and stored in the attached condenser over a set
Name Symbol Company period of time, the time constant (Table 7.5). The energy
accumulated during the time constant is the detector
Gamma ray log GR all value at that depth for that time constant. The too! liter-
ally ‘counts’ the gamma rays.
Spectralog SL Western Atlas
Naturaj gamma ray Spectral gamma ray tooi
spectrometry NGS Schlumberger The spectral gamma ray tool, like the simple tool,
Spectral gamma ray SGR, CSNG Halliburton consists of a scintillation counter and photo-multiplier.
However, in the spectra] tool, the sodium iodide crystal
Spectral gamma
has a much greater volume, typically 5 cm in diameter
sonde SGS B.P.B.
and 20 cm long and so gives the tool a much better
‘counting’ sensitivity. When a gamma ray passes through
Table 7.4 Ratios of radioactive to non-radioactive material in
normal elementat mixtures (Serra er al., $980). a scintillation crystal, it not only causes a flash, but the
intensity of that flash depends on the energy of the
40 K 22Th 238 U 235 U 234 U
incident gamma ray. This characteristic is used by the
spectral gamma ray tool, with its large scintillator crystal,
% radioactive isotopes
to identify the gamma radiations in several, pre-defined
in normal mixtures 0.0199 LOO 99.27 0.72 0.0057
energy bins or windows. These windows are designed to
separate the distinctive energy peaks of the individual
WK 238] 2351) Ly
— All radioactive elements discussed above (Figure 7.4),
namely bracketing the energies of 2.62 MeV for thorium,
Kw Urosat Vous Veena
1.76 MeV for uranium and 1.46 MeV for potassium. In
most tools the lower energy counts are also used and
at 1.76 Me¥ and thorium at 2.62 MeY still exist and can
‘allocated’ to each element.
be used to identify the original source of radiations. This
is the principle used in the spectral gamma ray tool
Table 7.5 Logging speed v. lime-constant — simple gamma
(Section 7.3). ray tool.
Time-constant Logging speed Formation logged
7.3 Tools
(seconds) (m/h)} in time-constant
Simple gamma ray tool (cm)
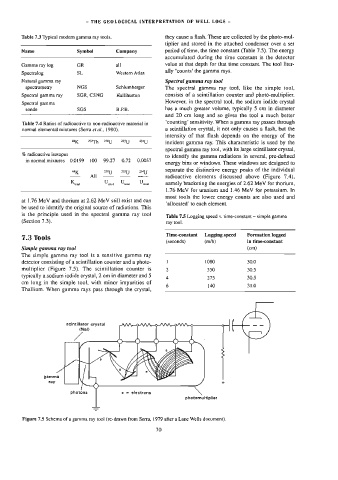
The simple gamma ray tool is a sensitive gamma ray
detector consisting of a scintillation counter and a photo- 1 L080 30.0
muluplier (Figure 7.5). The scintillation counter is 2 550 30.5
typically a sodium iodide crystal, 2 cm in diameter and 5
4 275 30.5
cm long in the simple tool, with minor impurities of
6 140 31.0
Thalliam. When gamma rays pass through the crystal,
scintillator crystal
{Nal}
gamma
ray
photons
photomultiplier
Figure 7.5 Schema of a gamma ray too] (re-drawn from Serta, 1979 after a Lane Wells document).