Page 106 - The Handbook for Quality Management a Complete Guide to Operational Excellence
P. 106
92 I n t e g r a t e d P l a n n i n g S t r a t e g i c P l a n n i n g 93
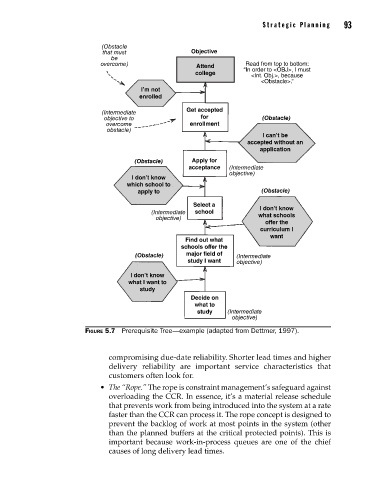
(Obstacle
that must Objective
be
overcome) Attend Read from top to bottom:
college “In order to <OBJ>, I must
<Int. Obj.>, because
<Obstacle>.”
I’m not
enrolled
(Intermediate Get accepted
objective to for (Obstacle)
overcome enrollment
obstacle)
I can’t be
accepted without an
application
(Obstacle) Apply for
acceptance (Intermediate
objective)
I don’t know
which school to
apply to (Obstacle)
Select a I don’t know
(Intermediate school what schools
objective)
offer the
curriculum I
want
Find out what
schools offer the
(Obstacle) major field of (Intermediate
study I want objective)
I don’t know
what I want to
study
Decide on
what to
study (Intermediate
objective)
Figure 5.7 Prerequisite Tree—example (adapted from Dettmer, 1997).
compromising due-date reliability. Shorter lead times and higher
delivery reliability are important service characteristics that
customers often look for.
• The “Rope.” The rope is constraint management’s safeguard against
overloading the CCR. In essence, it’s a material release schedule
that prevents work from being introduced into the system at a rate
faster than the CCR can process it. The rope concept is designed to
prevent the backlog of work at most points in the system (other
than the planned buffers at the critical protected points). This is
important because work-in-process queues are one of the chief
causes of long delivery lead times.
05_Pyzdek_Ch05_p061-102.indd 93 11/9/12 5:04 PM