Page 107 - The Handbook for Quality Management a Complete Guide to Operational Excellence
P. 107
94 I n t e g r a t e d P l a n n i n g S t r a t e g i c P l a n n i n g 95
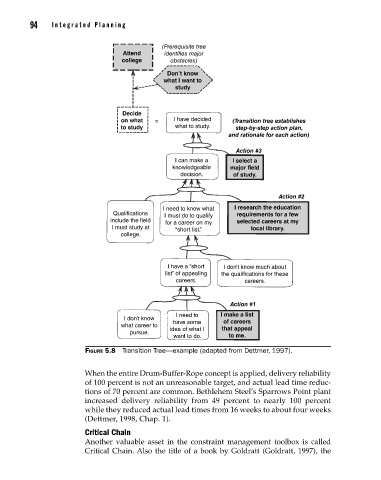
(Prerequisite tree
Attend identifies major
college obstacles)
Don’t know
what I want to
study
Decide
on what = I have decided (Transition tree establishes
to study what to study. step-by-step action plan,
and rationale for each action)
Action #3
I can make a I select a
knowledgeable major field
decision. of study.
Action #2
I need to know what I research the education
Qualifications I must do to qualify requirements for a few
include the field for a career on my selected careers at my
I must study at “short list.” local library.
college.
I have a “short I don’t know much about
list” of appealing the qualifications for these
careers. careers.
Action #1
I need to I make a list
I don’t know of careers
what career to have some that appeal
pursue. idea of what I
want to do. to me.
Figure 5.8 Transition Tree—example (adapted from Dettmer, 1997).
When the entire Drum-Buffer-Rope concept is applied, delivery reliability
of 100 percent is not an unreasonable target, and actual lead time reduc-
tions of 70 percent are common. Bethlehem Steel’s Sparrows Point plant
increased delivery reliability from 49 percent to nearly 100 percent
while they reduced actual lead times from 16 weeks to about four weeks
(Dettmer, 1998, Chap. 1).
Critical Chain
Another valuable asset in the constraint management toolbox is called
Crit ical Chain. Also the title of a book by Goldratt (Goldratt, 1997), the
05_Pyzdek_Ch05_p061-102.indd 94 11/9/12 5:04 PM