Page 187 - The Handbook for Quality Management a Complete Guide to Operational Excellence
P. 187
174 P r o c e s s C o n t r o l Q u a n t i f y i n g P r o c e s s Va r i a t i o n 175
Distribution of
averages
Distribution of
individual
observations
Target New mean
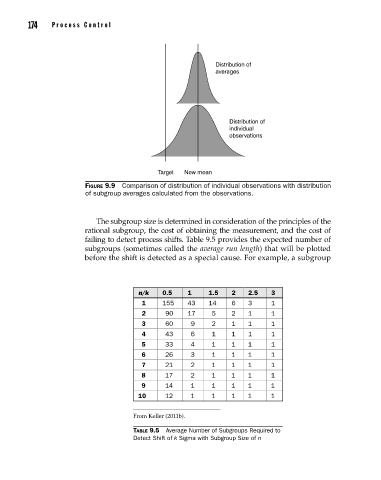
Figure 9.9 Comparison of distribution of individual observations with distribution
of subgroup averages calculated from the observations.
The subgroup size is determined in consideration of the principles of the
rational subgroup, the cost of obtaining the measurement, and the cost of
failing to detect process shifts. Table 9.5 provides the expected number of
subgroups (sometimes called the average run length) that will be plotted
before the shift is detected as a special cause. For example, a subgroup
n/k 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3
1 155 43 14 6 3 1
2 90 17 5 2 1 1
3 60 9 2 1 1 1
4 43 6 1 1 1 1
5 33 4 1 1 1 1
6 26 3 1 1 1 1
7 21 2 1 1 1 1
8 17 2 1 1 1 1
9 14 1 1 1 1 1
10 12 1 1 1 1 1
From Keller (2011b).
Table 9.5 Average Number of Subgroups Required to
Detect Shift of k Sigma with Subgroup Size of n
09_Pyzdek_Ch09_p151-208.indd 174 11/21/12 1:42 AM