Page 43 - The Tribology Handbook
P. 43
A7 Grease, wick and drip fed journal bearings
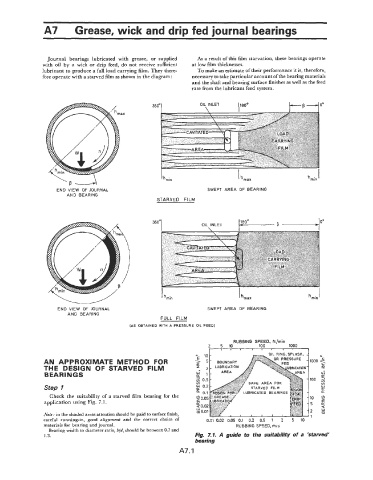
Journal bearings lubricated with grease, or supplied As a result of this film starvation, these bearings operate
with oil by a wick or drip feed, do not receive sufficient at low film thicknesses.
lubricant to produce a full load carrying film. They there- To make an estimate of their performance it is, therefore,
fore operate with a starved film as shown in the diagram: necessary to take particular account of the bearing materials
and the shaft and bearing surface finishes as well as the feed
rate from the lubricant feed system.
360'1 OIL INLET (180°
hmin I
I I
END VIEW OF JOURNAL SWEPT AREA OF BEARING
AND BEARING
STARVED FILM
I I I
END VIEW OF JOURNAL SWEPT AREA OF BEARING
AND BEARING
FULL FILM
[AS OBTAINED WITH A PRESSURE OIL FEED1
RUBBING SPEED, ft/rnin
2 5 10 100 1000
i , I I
AN APPROXIMATE METHOD FOR
THE DESIGN OF STARVED FILM
BEARINGS
Step 1
Check the suitability of a starved film bearing for the
application using Fig. 7.1.
Note: in the shaded areas attention should be paid to surface finish,
careful running-in, good alignment and the correct choice of 0.01 0.02 0.05 0.1 0.2 0.5 1 2 5 10
materials for bearing and journal. RUBBING SPEED, mls
Bearing width to diameter ratio, b/d, should be between 0.7 and
1.3. Fig. 7.1. A guide to the suitability of a 'starved'
bearing
A7.1