Page 77 - The Tribology Handbook
P. 77
AI 2 Plain bearing form and installation
METHODS OF MEASUREMENT AND CHOICE OF HOUSING FITS
Ferrous-backed bearings in ferrous housings
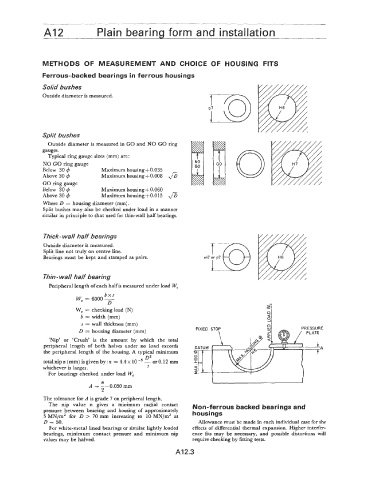
Solid bushes
Outside diameter is measured.
Split bushes
Outside diameter is measured in GO and NO GO ring
gauges.
Typical ring gauge sizes (mm) are:
NO GO ring gauge
Below 30 r$ Maximum housing+ 0.035
Above 30 #I Maximum housing+0.008 fi
GO ring gauge
Below 30 r$ Maximum housing + 0.060
Above 30 4 Maximum housingf0.015 fi
Where D = housing diameter (mm).
Split bushes may also be checked under load in a manner
similar in principle to that used for thin-wall half bearings.
Thick- wall half bearings
Outside diameter is measured.
Split line not truly on centre line.
Bearings must be kept and stamped as pairs. mJ or p7
Thin- wall half bearing
Peripheral length of each half is measured under load W,
bxs
w, = 6000 -
D
W, = checking load (N)
b = width (mm)
s = wall thickness (mm)
D = housing diameter (mm) PRESSURE
'Nip' or 'Crush' is the amount by which the total
peripheral length of both halves under no load exceeds
the peripheral length of the housing. A typical minimum
02
total nip n (mm) is given by : n = 4.4 x 10 -' -or 0.12 mm
whichever is large].. S
For bearings checked under load W,
A = :-0.050 mm
2
-
..
The tolerance for A is grade 7 on peripheral length.
I
The nip value n gives a minimum radial contact Non-ferrous backed bearings and
pressure between bearing and housing of approximately housings
5 MN/m2 for D > 70 mm increasine to 10 MN/m2 at
"
D = 50. Allowance must be made in each individual case for the
For white-metal lined bearings or similar lightly loaded effects of differential thermal expansion. Higher interfer-
bearings, minimum contact pressure and minimum nip ence fits may be necessary, and possible distortions will
values may be halved. require checking by fitting tests.
AI 2.3