Page 336 - Thermal Hydraulics Aspects of Liquid Metal Cooled Nuclear Reactors
P. 336
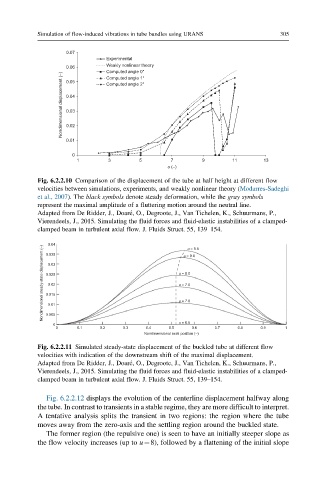
Simulation of flow-induced vibrations in tube bundles using URANS 305
0.07
Experimental
0.06 Weakly nonlinear theory
Computed angle 0°
Nondimensional displacement (–) 0.04
Computed angle 1°
0.05
Computed angle 2°
0.03
0.02
0.01
0
1 3 5 7 9 11 13
u (–)
Fig. 6.2.2.10 Comparison of the displacement of the tube at half height at different flow
velocities between simulations, experiments, and weakly nonlinear theory (Modarres-Sadeghi
et al., 2007). The black symbols denote steady deformation, while the gray symbols
represent the maximal amplitude of a fluttering motion around the neutral line.
Adapted from De Ridder, J., Doar e, O., Degroote, J., Van Tichelen, K., Schuurmans, P.,
Vierendeels, J., 2015. Simulating the fluid forces and fluid-elastic instabilities of a clamped-
clamped beam in turbulent axial flow. J. Fluids Struct. 55, 139–154.
0.04 u = 9.0
Nondimensional steady-state displacement (–) 0.025 u = 8.0
u = 9.5
0.035
0.03
0.02
u = 7.5
0.015
u = 7.0
0.01
0.005
0 u = 6.5
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 0.7 0.8 0.9 1
Nondimensional axial position (–)
Fig. 6.2.2.11 Simulated steady-state displacement of the buckled tube at different flow
velocities with indication of the downstream shift of the maximal displacement.
Adapted from De Ridder, J., Doar e, O., Degroote, J., Van Tichelen, K., Schuurmans, P.,
Vierendeels, J., 2015. Simulating the fluid forces and fluid-elastic instabilities of a clamped-
clamped beam in turbulent axial flow. J. Fluids Struct. 55, 139–154.
Fig. 6.2.2.12 displays the evolution of the centerline displacement halfway along
the tube. In contrast to transients in a stable regime, they are more difficult to interpret.
A tentative analysis splits the transient in two regions: the region where the tube
moves away from the zero-axis and the settling region around the buckled state.
The former region (the repulsive one) is seen to have an initially steeper slope as
the flow velocity increases (up to u¼8), followed by a flattening of the initial slope