Page 337 - Thermal Hydraulics Aspects of Liquid Metal Cooled Nuclear Reactors
P. 337
306 Thermal Hydraulics Aspects of Liquid Metal Cooled Nuclear Reactors
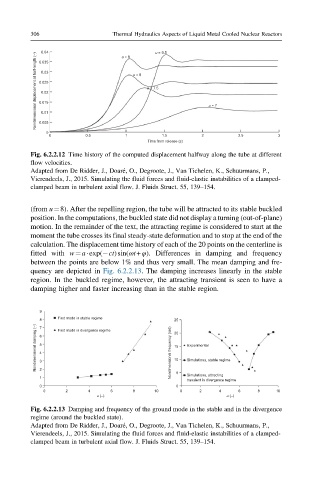
0.04 u = 9 u = 9.5
Nondimensional displacement at half-length (–) 0.025 u = 8 u = 7.5 u = 7
0.035
0.03
0.02
0.015
0.01
0.005
0
0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3
Time from release (s)
Fig. 6.2.2.12 Time history of the computed displacement halfway along the tube at different
flow velocities.
Adapted from De Ridder, J., Doar e, O., Degroote, J., Van Tichelen, K., Schuurmans, P.,
Vierendeels, J., 2015. Simulating the fluid forces and fluid-elastic instabilities of a clamped-
clamped beam in turbulent axial flow. J. Fluids Struct. 55, 139–154.
(from u¼8). After the repelling region, the tube will be attracted to its stable buckled
position. In the computations, the buckled state did not display a turning (out-of-plane)
motion. In the remainder of the text, the attracting regime is considered to start at the
moment the tube crosses its final steady-state deformation and to stop at the end of the
calculation. The displacement time history of each of the 20 points on the centerline is
fitted with w¼a exp( ct)sin(ωt+φ). Differences in damping and frequency
between the points are below 1% and thus very small. The mean damping and fre-
quency are depicted in Fig. 6.2.2.13. The damping increases linearly in the stable
region. In the buckled regime, however, the attracting transient is seen to have a
damping higher and faster increasing than in the stable region.
9
First mode in stable regime
8 7 First mode in divergence regime 25
Nondimensional damping (–) 6 5 4 3 Nondimensional frequency (rad) 15 Experimental
20
Simulations, stable regime
10
1 2 5 Simulations, attracting
transient in divergence regime
0 0
0 2 4 6 8 10 0 2 4 6 8 10
u (–) u (–)
Fig. 6.2.2.13 Damping and frequency of the ground mode in the stable and in the divergence
regime (around the buckled state).
Adapted from De Ridder, J., Doar e, O., Degroote, J., Van Tichelen, K., Schuurmans, P.,
Vierendeels, J., 2015. Simulating the fluid forces and fluid-elastic instabilities of a clamped-
clamped beam in turbulent axial flow. J. Fluids Struct. 55, 139–154.