Page 123 - Wind Energy Handbook
P. 123
THE AERODYNAMICS OF A WIND TURBINE IN STEADY YAW 97
z
y
x
γ
U
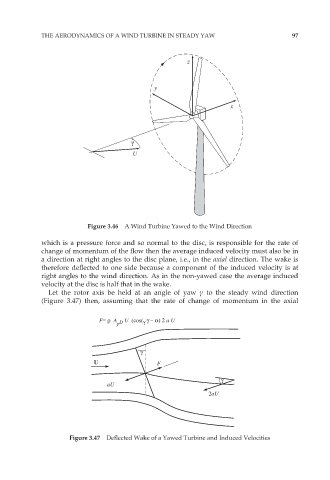
Figure 3.46 A Wind Turbine Yawed to the Wind Direction
which is a pressure force and so normal to the disc, is responsible for the rate of
change of momentum of the flow then the average induced velocity must also be in
a direction at right angles to the disc plane, i.e., in the axial direction. The wake is
therefore deflected to one side because a component of the induced velocity is at
right angles to the wind direction. As in the non-yawed case the average induced
velocity at the disc is half that in the wake.
Let the rotor axis be held at an angle of yaw ª to the steady wind direction
(Figure 3.47) then, assuming that the rate of change of momentum in the axial
F= ρ A U (cos( γ – α) 2 a U
p D γ
γ
U F
γ
aU
2aU
Figure 3.47 Deflected Wake of a Yawed Turbine and Induced Velocities