Page 40 - Wire Bonding in Microelectronics
P. 40
Ultrasonic Bonding Systems and Technologies 19
–10 –10
0 0
10 10
20 20
60 kHz
80 kHz
30 30
40 40
50 50
60 60
–4 –3 –2 –1 0 1 2 –2 –1 0 1 2 3 4
Amplitude Amplitude
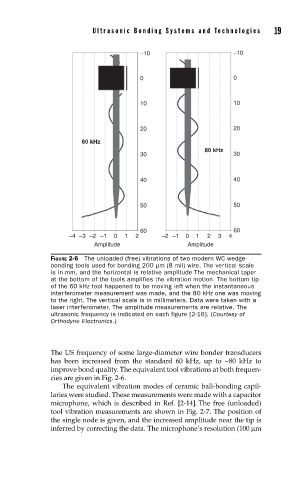
FIGURE 2-6 The unloaded (free) vibrations of two modern WC wedge-
bonding tools used for bonding 200 µm (8 mil) wire. The vertical scale
is in mm, and the horizontal is relative amplitude The mechanical taper
at the bottom of the tools amplifies the vibration motion. The bottom tip
of the 60 kHz tool happened to be moving left when the instantaneous
interferometer measurement was made, and the 80 kHz one was moving
to the right. The vertical scale is in millimeters. Data were taken with a
laser interferometer. The amplitude measurements are relative. The
ultrasonic frequency is indicated on each figure [2-16]. (Courtesy of
Orthodyne Electronics.)
The US frequency of some large-diameter wire bonder transducers
has been increased from the standard 60 kHz, up to ~80 kHz to
improve bond quality. The equivalent tool vibrations at both frequen-
cies are given in Fig. 2-6.
The equivalent vibration modes of ceramic ball-bonding capil-
laries were studied. These measurements were made with a capacitor
microphone, which is described in Ref. [2-14]. The free (unloaded)
tool vibration measurements are shown in Fig. 2-7. The position of
the single node is given, and the increased amplitude near the tip is
inferred by correcting the data. The microphone’s resolution (100 µm