Page 294 - Characterization and Properties of Petroleum Fractions - M.R. Riazi
P. 294
QC: —/—
P2: KVU/KXT
P1: KVU/KXT
AT029-06
AT029-Manual-v7.cls
AT029-Manual
June 22, 2007
20:46
274 CHARACTERIZATION AND PROPERTIES OF PETROLEUM FRACTIONS
300
4 500
30
10 T1: IML 4 50 6 7 8 9100 Pressure, PSIA 6 7 8 91,000 3,000 6 7 8 9 10,000
100 2 2 2 4 100
9 9
8 8
7 7
6 6
5 5
4 4
3 3
2 2
10 10
9 9
8 8
7 7
6 Temperature °F 6
5 5
4 500 4
450
3 400 3
350
2 300 2
1.0 200 1.0
9 180 9
8 160 8
7 7
6 140 6
5 120 5 --`,```,`,``````,`,````,```,,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---
4 100 4
K = y /x 3 80 3 K = y /x
2 60 2
0.1 40 0.1
20
9 9
8 8
7
0 7
6 6
5 5
4 –20 4
3 –40 3
2 2
.01 .01
9 9
8 8
7 7
6 6
5 5
4 4
3 3
2 2
.001 .001
10 2 30 4 50 6 7 8 9 100 2 300 4 500 67 8 91,000 2 3,000 4 67 8 9 10,000
Pressure, PSIA i - Butane
CONV. PRESS. 10,000 PSIA
◦
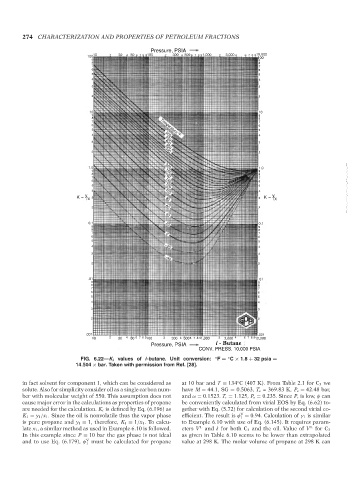
FIG. 6.22—K i values of i-butane. Unit conversion: ◦ F = C × 1.8 + 32 psia =
14.504 × bar. Taken with permission from Ref. [28].
in fact solvent for component 1, which can be considered as at 10 bar and T = 134 C (407 K). From Table 2.1 for C 3 we
◦
solute. Also for simplicity consider oil as a single carbon num- have M = 44.1, SG = 0.5063, T c = 369.83 K, P c = 42.48 bar,
ber with molecular weight of 550. This assumption does not and ω = 0.1523. T r = 1.125, P r = 0.235. Since P r is low, φ can
cause major error in the calculations as properties of propane be conveniently calculated from virial EOS by Eq. (6.62) to-
are needed for the calculation. K i is defined by Eq. (6.196) as gether with Eq. (5.72) for calculation of the second virial co-
V
K 1 = y 1 /x 1 . Since the oil is nonvolatile thus the vapor phase efficient. The result is φ = 0.94. Calculation of γ 1 is similar
1
is pure propane and y 1 = 1, therefore, K 1 = 1/x 1 . To calcu- to Example 6.10 with use of Eq. (6.145). It requires param-
L
L
late x 1 , a similar method as used in Example 6.10 is followed. eters V and δ for both C 3 and the oil. Value of V for C 3
In this example since P = 10 bar the gas phase is not ideal as given in Table 6.10 seems to be lower than extrapolated
V
and to use Eq. (6.179), φ must be calculated for propane value at 298 K. The molar volume of propane at 298 K can
1
Copyright ASTM International
Provided by IHS Markit under license with ASTM Licensee=International Dealers Demo/2222333001, User=Anggiansah, Erick
No reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS Not for Resale, 08/26/2021 21:56:35 MDT