Page 299 - Characterization and Properties of Petroleum Fractions - M.R. Riazi
P. 299
P2: KVU/KXT
QC: —/—
P1: KVU/KXT
AT029-Manual
AT029-Manual-v7.cls
AT029-06
20:46
June 22, 2007
Pressure, PSIA
67 8 9 1,000
6 7 8 9 10,000
4 500
10 T1: IML 30 6. THERMODYNAMIC RELATIONS FOR PROPERTY ESTIMATIONS 279
4 50
67 8 9100
3,000
300
2
4
10 2 2 10
9 9
8 8
7 7
6 6
5 5
4 4
3 3
2 2
1.0 Temperature °F 1.0
500
9 9
8 450 8
7 7
6 6
5 400 5
4 4
3 3
2 300 2
280
0.1 260 0.1
240
9 9
8 220 8
7 7
6 200 6
5 5
4 180 4
K = y /x 3 160 3 K = y /x
2 140 2
120
.01 100 .01
9 9
8 8
7 80 7
6 6
5 5
60
4 4
3 3
40
2 2
20
.001 .001
9 9
8 0 8
7 7
6 6
5 5
4 –20 4
3 3
2 2
–40
.0001 .0001
10 2 30 4 50 67 8 9 100 2 300 4 500 67 8 9 1,000 2 3,000 4 67 8 9 10,000
Pressure, PSIA Heptane
CONV. PRESS. 10,000 PSIA
◦
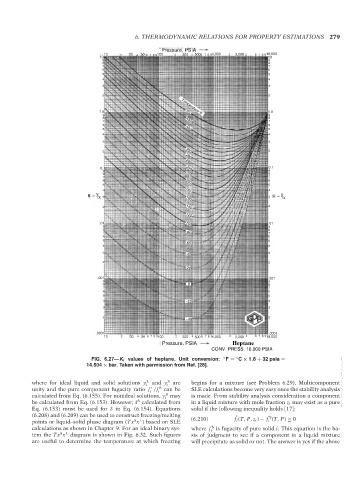
FIG. 6.27—K i values of heptane. Unit conversion: ◦ F = C × 1.8 + 32 psia =
14.504 × bar. Taken with permission from Ref. [28].
where for ideal liquid and solid solutions γ L and γ S are begins for a mixture (see Problem 6.29). Multicomponent --`,```,`,``````,`,````,```,,-`-`,,`,,`,`,,`---
i i
L
unity and the pure component fugacity ratio f /f S can be SLE calculations become very easy once the stability analysis
i i
S
calculated from Eq. (6.155). For nonideal solutions, γ may is made. From stability analysis consideration a component
i
S
be calculated from Eq. (6.153). However, δ calculated from in a liquid mixture with mole fraction z i may exist as a pure
Eq. (6.153) must be used for δ in Eq. (6.154). Equations solid if the following inequality holds [17]:
(6.208) and (6.209) can be used to construct freezing/melting ˆ S
S L
points or liquid–solid phase diagram (Tx x ) based on SLE (6.210) f i (T, P, z i ) − f (T, P) ≥ 0
i
S
calculations as shown in Chapter 9. For an ideal binary sys- where f is fugacity of pure solid i. This equation is the ba-
i
S L
tem the Tx x diagram is shown in Fig. 6.32. Such figures sis of judgment to see if a component in a liquid mixture
are useful to determine the temperature at which freezing will precipitate as solid or not. The answer is yes if the above
Copyright ASTM International
Provided by IHS Markit under license with ASTM Licensee=International Dealers Demo/2222333001, User=Anggiansah, Erick
No reproduction or networking permitted without license from IHS Not for Resale, 08/26/2021 21:56:35 MDT