Page 109 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 109
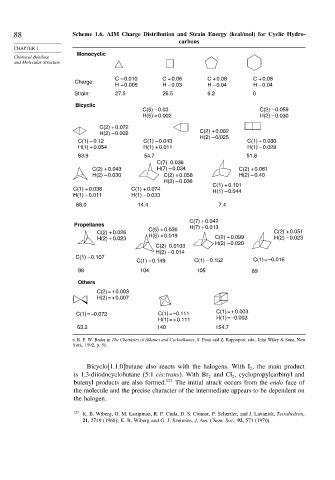
88 Scheme 1.6. AIM Charge Distribution and Strain Energy (kcal/mol) for Cyclic Hydro-
carbons
CHAPTER 1
Monocyclic
Chemical Bonding
and Molecular Structure
C – 0.010 C + 0.06 C + 0.08 C + 0.08
Charge:
H + 0.005 H – 0.03 H – 0.04 H – 0.04
Strain: 27.5 26.5 6.2 0
Bicyclic
C(5) – 0.03 C(2) – 0.059
H(5) + 0.002 H(2) – 0.030
C(2) + 0.072
C(2) + 0.082
H(2) – 0.002
H(2) – 0/025
C(1) – 0.12 C(1) – 0.043 C(1) + 0.030
H(1) + 0.054 H(1) + 0.011 H(1) – 0.028
63.9 54.7 51.8
C(7) 0.036
C(2) + 0.043 H(7) – 0.034 C(2) + 0.061
H(2) – 0.030 C(2) + 0.058 H(2) – 0.40
H(2) – 0.036
C(1) + 0.101
C(1) + 0.036 C(1) + 0.074 H(1) – 0.044
H(1) – 0.011 H(1) – 0.033
68.0 14.4 7.4
C(7) + 0.042
Propellanes
C(5) + 0.036 H(7) + 0.013
C(2) + 0.026 C(2) + 0.051
H(2) + 0.023 H(5) + 0.019 C(2) + 0.099 H(2) – 0.023
H(2) – 0.020
C(2) 0.0103
H(2) – 0.014
C(1) – 0.107
C(1) – 0.149 C(1) – 0.152 C(1) = –0.016
98 104 105 89
Others
C(2) = + 0.003
H(2) = + 0.007
C(1) = –0.072 C(1) = –0.111 C(1) = + 0.003
H(1) = + 0.111 H(1) = –0.003
63.2 140 154.7
a. R. F. W. Bader in The Chemistry of Alkanes and Cycloalkanes, S. Patai and Z. Rappoport, eds., John Wiley & Sons, New
York, 1992, p. 51.
Bicyclo[1.1.0]butane also reacts with the halogens. With I , the main product
2
is 1,3-diiodocyclobutane (5:1 cis:trans). With Br and Cl , cyclopropylcarbinyl and
2
2
butenyl products are also formed. 127 The initial attack occurs from the endo face of
the molecule and the precise character of the intermediate appears to be dependent on
the halogen.
127
K. B. Wiberg, G. M. Lampman, R. P. Ciula, D. S. Connor, P. Schertler, and J. Lavanish, Tetrahedron,
21, 2749 (1968); K. B. Wiberg and G. J. Szeimies, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 92, 571 (1970).