Page 1105 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 1105
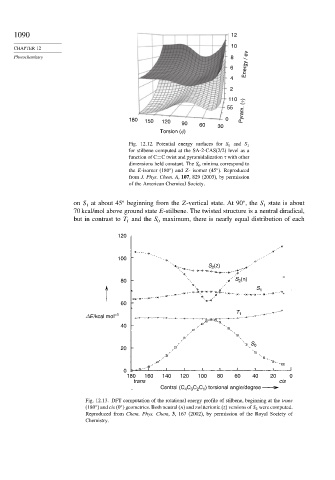
1090 12
10
CHAPTER 12
Energy / ev
Photochemistry 8
6
4
2
110
55 Pyram. (τ)
180 150 120 90 60 0
Torsion (φ) 30
Fig. 12.12. Potential energy surfaces for S 0 and S 1
for stilbene computed at the SA-2-CAS(2/2) level as a
function of C=C twist and pyramidalization with other
dimensions held constant. The S 0 minima correspond to
the E-isomer (180 ) and Z- isomer (45 ). Reproduced
from J. Phys. Chem. A, 107, 829 (2003), by permission
of the American Chemical Society.
on S at about 45 beginning from the Z-vertical state. At 90 , the S state is about
1
1
70 kcal/mol above ground state E-stilbene. The twisted structure is a neutral diradical,
but in contrast to T and the S maximum, there is nearly equal distribution of each
0
1
120
100
S (z)
2
80 S (n)
2
S 1
60
T 1
ΔE /kcal mol –1
40
S 0
20
0
180 160 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 0
trans cis
C C C ) torsional angle/degree
Central (C 4 3 2 1
Fig. 12.13. DFT computation of the rotational energy profile of stilbene, beginning at the trans
(180 ) and cis (0 ) geometries. Both neutral (n) and zwitterionic (z) versions of S 2 were computed.
Reproduced from Chem. Phys. Chem, 3, 167 (2002), by permission of the Royal Society of
Chemistry.