Page 1155 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 1155
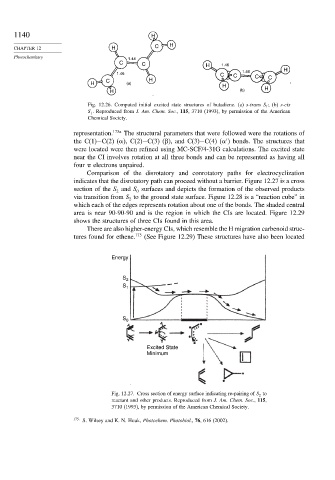
1140 H
CHAPTER 12 H C H
Photochemistry 1.44
C C H 1.46
H
1.46
1.46 C C C
C H C
H (a)
H
H (b) H
Fig. 12.26. Computed initial excited state structures of butadiene. (a) s-trans S 1 ; (b) s-cis
S 1 . Reproduced from J. Am. Chem. Soc., 115, 3710 (1993), by permission of the American
Chemical Society.
representation. 173a The structural parameters that were followed were the rotations of
the C(1)−C(2) ( , C(2)−C(3) (
), and C(3)−C(4) ( ) bonds. The structures that
were located were then refined using MC-SCF/4-31G calculations. The excited state
near the CI involves rotation at all three bonds and can be represented as having all
four electrons unpaired.
Comparison of the disrotatory and conrotatory paths for electrocyclization
indicates that the disrotatory path can proceed without a barrier. Figure 12.27 is a cross
section of the S and S surfaces and depicts the formation of the observed products
0
2
via transition from S to the ground state surface. Figure 12.28 is a “reaction cube” in
2
which each of the edges represents rotation about one of the bonds. The shaded central
area is near 90-90-90 and is the region in which the CIs are located. Figure 12.29
shows the structures of three CIs found in this area.
There are also higher-energy CIs, which resemble the H migration carbenoid struc-
tures found for ethene. 175 (See Figure 12.29) These structures have also been located
Energy
S 2
S 1
S 0
Excited State
Minimum
Fig. 12.27. Cross section of energy surface indicating re-pairing of S 2 to
reactant and other products. Reproduced from J. Am. Chem. Soc., 115,
3710 (1993), by permission of the American Chemical Society.
175
S. Wilsey and K. N. Houk, Photochem. Photobiol., 76, 616 (2002).