Page 267 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 267
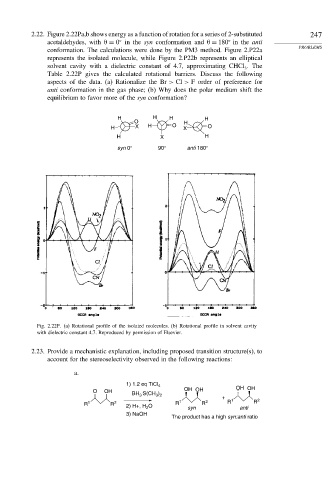
2.22. Figure 2.22Pa,b shows energy as a function of rotation for a series of 2-substituted 247
acetaldehydes, with
= 0 in the syn conformation and
= 180 in the anti
PROBLEMS
conformation. The calculations were done by the PM3 method. Figure 2.P22a
represents the isolated molecule, while Figure 2.P22b represents an elliptical
solvent cavity with a dielectric constant of 4.7, approximating CHCl . The
3
Table 2.22P gives the calculated rotational barriers. Discuss the following
aspects of the data. (a) Rationalize the Br > Cl > F order of preference for
anti conformation in the gas phase; (b) Why does the polar medium shift the
equilibrium to favor more of the syn conformation?
H H H H
O H
H X H O X O
H X H
syn 0° 90° anti 180°
Fig. 2.22P. (a) Rotational profile of the isolated molecules. (b) Rotational profile in solvent cavity
with dielectric constant 4.7. Reproduced by permission of Elsevier.
2.23. Provide a mechanistic explanation, including proposed transition structure(s), to
account for the stereoselectivity observed in the following reactions:
a.
1) 1.2 eq TiCl 4
O OH BH S(CH ) OH OH OH OH
.
3 2
3
+ 1 2
R 1 R 2 2) H+, H O R 1 syn R 2 R anti R
2
3) NaOH
The product has a high syn:anti ratio