Page 264 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 264
244 c. The biosynthesis of valine by bacteria involves the following sequence:
O
CHAPTER 2
(CH 3 ) 2 C CHCO H (CH ) CHCHCO H
Stereochemistry, 2 (CH ) CHCCO H 3 2 2
3 2
2
Conformation,
and Stereoselectivity OH OH NH 2
The stereochemistry of the reaction has been examined using the starting diol
in which each methyl group was separately replaced by CD . The diol-d of
3
3
the 2R,3R configuration produces 2S,3S-valine-d , whereas the 2R,3S diol-d
3 3
produces 2S,3R-valine-d . From this information deduce whether the C(2)
3
and C(3) hydroxy are replaced with inversion or retention of configuration.
Show the basis for your conclusion.
d. A synthesis of the important biosynthetic intermediate mevalonic acid starts
with the enzymatic hydrolysis of the diester 14-C by pig liver esterase.
The pro-R ester group is selectively hydrolyzed. Draw a three-dimensional
structure of the product.
CH 3
H CO CCH CCH CO CH 3
2
3
2
2
2
OH
14-C
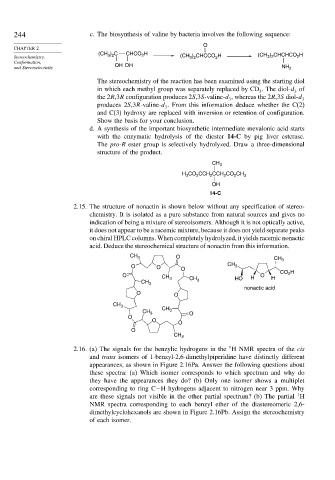
2.15. The structure of nonactin is shown below without any specification of stereo-
chemistry. It is isolated as a pure substance from natural sources and gives no
indication of being a mixture of stereoisomers. Although it is not optically active,
it does not appear to be a racemic mixture, because it does not yield separate peaks
on chiral HPLC columns. When completely hydrolyzed, it yields racemic nonactic
acid. Deduce the stereochemical structure of nonactin from this information.
CH 3 O
CH 3
O O O CH 3
2
O CH 3 CH HO H O H CO H
CH 3 3
nonactic acid
O O
CH 3
CH 3 CH 3 O
O
O
O
O
CH 3
1
2.16. (a) The signals for the benzylic hydrogens in the H NMR spectra of the cis
and trans isomers of 1-benzyl-2,6-dimethylpiperidine have distinctly different
appearances, as shown in Figure 2.16Pa. Answer the following questions about
these spectra: (a) Which isomer corresponds to which spectrum and why do
they have the appearances they do? (b) Only one isomer shows a multiplet
corresponding to ring C−H hydrogens adjacent to nitrogen near 3 ppm. Why
1
are these signals not visible in the other partial spectrum? (b) The partial H
NMR spectra corresponding to each benzyl ether of the diastereomeric 2,6-
dimethylcyclohexanols are shown in Figure 2.16Pb. Assign the stereochemistry
of each isomer.