Page 309 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 309
290
CHAPTER 3 transition state
transition state
Structural Effects on
Stability and Reactivity transition state
I or P
R
R
R
I or P I or P
case (a) case (b) case (c)
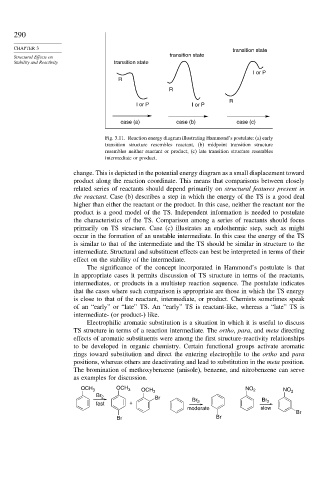
Fig. 3.11. Reaction energy diagram illustrating Hammond’s postulate: (a) early
transition structure resembles reactant, (b) midpoint transition structure
resembles neither reactant or product, (c) late transition structure resembles
intermediate or product.
change. This is depicted in the potential energy diagram as a small displacement toward
product along the reaction coordinate. This means that comparisons between closely
related series of reactants should depend primarily on structural features present in
the reactant. Case (b) describes a step in which the energy of the TS is a good deal
higher than either the reactant or the product. In this case, neither the reactant nor the
product is a good model of the TS. Independent information is needed to postulate
the characteristics of the TS. Comparison among a series of reactants should focus
primarily on TS structure. Case (c) illustrates an endothermic step, such as might
occur in the formation of an unstable intermediate. In this case the energy of the TS
is similar to that of the intermediate and the TS should be similar in structure to the
intermediate. Structural and substituent effects can best be interpreted in terms of their
effect on the stability of the intermediate.
The significance of the concept incorporated in Hammond’s postulate is that
in appropriate cases it permits discussion of TS structure in terms of the reactants,
intermediates, or products in a multistep reaction sequence. The postulate indicates
that the cases where such comparison is appropriate are those in which the TS energy
is close to that of the reactant, intermediate, or product. Chemists sometimes speak
of an “early” or “late” TS. An “early” TS is reactant-like, whereas a “late” TS is
intermediate- (or product-) like.
Electrophilic aromatic substitution is a situation in which it is useful to discuss
TS structure in terms of a reaction intermediate. The ortho, para, and meta directing
effects of aromatic substituents were among the first structure-reactivity relationships
to be developed in organic chemistry. Certain functional groups activate aromatic
rings toward substitution and direct the entering electrophile to the ortho and para
positions, whereas others are deactivating and lead to substitution in the meta position.
The bromination of methoxybenzene (anisole), benzene, and nitrobenzene can serve
as examples for discussion.
OCH 3 OCH 3 OCH 3 NO 2 NO 2
Br 2 Br Br
fast + Br 2 2
moderate slow
Br
Br Br