Page 345 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 345
326
CHAPTER 3 1.377
1.863 1.392 1.409
Structural Effects on 1.431 2.027
Stability and Reactivity 2.235 0.980 1.254
1.369 1.232 1.472
2.470 1.420 1.531
1.254
1.224 1.523
2.318 1.392
1.510
(a) TS2a
(a) TS3a –
CH COOCH + HO – CH COOCH + HO
3
3
3 3
(a) TS1a
TS3a
–15.7 15.7
TS1a –17.0 image of TSIa
1.1 –1.1
17.0 image of HBRIa
HBR1a –13.9 TS2a
13.9
6.9
image of INTa
–
INTa CH COO + CH OH
1.439 3 3
2.251
1.362 –32.5
2.983
17.1
1.221
1.952 1.491 1.404
1.508 HBPa
(a) HBR1a 1.501 1.289
1.542
(a) INTa
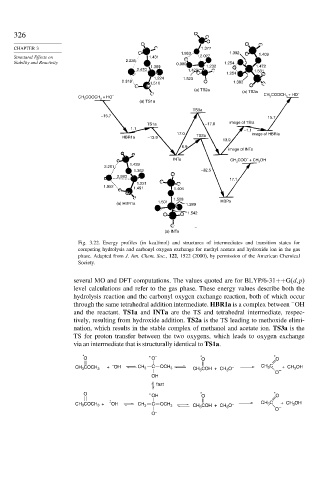
Fig. 3.22. Energy profiles (in kcal/mol) and structures of intermediates and transition states for
competing hydrolysis and carbonyl oxygen exchange for methyl acetate and hydroxide ion in the gas
phase. Adapted from J. Am. Chem. Soc., 122, 1522 (2000), by permission of the American Chemical
Society.
several MO and DFT computations. The values quoted are for BLYP/6-31++G(d,p)
level calculations and refer to the gas phase. These energy values describe both the
hydrolysis reaction and the carbonyl oxygen exchange reaction, both of which occur
−
through the same tetrahedral addition intermediate. HBR1a is a complex between OH
and the reactant. TS1a and INTa are the TS and tetrahedral intermediate, respec-
tively, resulting from hydroxide addition. TS2a is the TS leading to methoxide elimi-
nation, which results in the stable complex of methanol and acetate ion. TS3a is the
TS for proton transfer between the two oxygens, which leads to oxygen exchange
via an intermediate that is structurally identical to TS1a.
* – * *
O * O O O
–
+ OH C CH 3 C + CH 3 OH
CH 3 COCH 3 CH 3 OCH 3 CH 3 COH + CH 3 O – –
O
OH
fast
O * OH * O * O
– * CH 3 C
CH 3 COCH 3 + OH CH 3 C OCH 3 CH 3 COH + CH 3 O – + CH 3 OH
O –
O –