Page 701 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 701
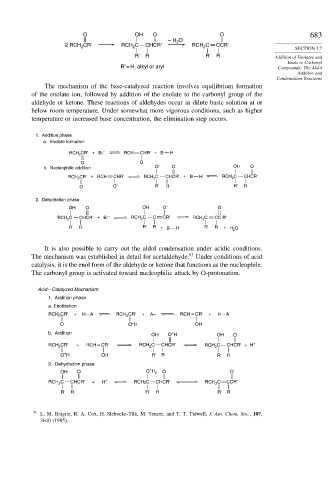
O OH O O 683
– H O
2
2 RCH CR' RCH C CHCR' RCH C CCR'
2
2
2
SECTION 7.7
R' R R' R Addition of Enolates and
Enols to Carbonyl
R' = H, alkyl or aryl Compounds: The Aldol
Addition and
Condensation Reactions
The mechanism of the base-catalyzed reaction involves equilibrium formation
of the enolate ion, followed by addition of the enolate to the carbonyl group of the
aldehyde or ketone. These reactions of aldehydes occur in dilute basic solution at or
below room temperature. Under somewhat more vigorous conditions, such as higher
temperature or increased base concentration, the elimination step occurs.
1. Addition phase
a. Enolate formation
RCH 2 CR' + B: – RCH CHR' + B H
O O –
b. Nucleophilic addition O – O OH O
RCH 2 CR' + RCH CHR' RCH 2 C CHCR' + B H RCH 2 C CHCR'
O O – R' R R' R
2. Dehydration phase
OH O OH O – O
RCH 2 C CHCR' + B: – RCH 2 C C CR' RCH 2 C CC R'
R' R R' R + B H R' R + H 2 O
It is also possible to carry out the aldol condensation under acidic conditions.
93
The mechanism was established in detail for acetaldehyde. Under conditions of acid
catalysis, it is the enol form of the aldehyde or ketone that functions as the nucleophile.
The carbonyl group is activated toward nucleophilic attack by O-protonation.
Acid – Catalyzed Mechanism
1. Addition phase
a. Enolization
RCH CR' + H – A RCH CR' + A– RCH = CR' + H – A
2
2
+
O O H OH
b. Addition OH O H OH O
+
RCH CR' + RCH = CR' RCH C CHCR' RCH C CHCR' + H +
2
2
2
+
O H OH R' R R' R
2. Dehydration phase
+
OH O O H 2 O O
RCH C CHCR' + H + RCH2C CHCR' RCH C CCR'
2
2
R' R R' R R' R
93
L. M. Baigrie, R. A. Cox, H. Slebocka-Tilk, M. Tencer, and T. T. Tidwell, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 107,
3640 (1985).