Page 715 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 715
These and similar catalysts are effective with silyl ketene acetals and silyl ketene 697
thioacetals. 125
SECTION 7.7
Addition of Enolates and
Enols to Carbonyl
O N O Compounds: The Aldol
Addition and
N Cu N Condensation Reactions
OTMS Ph OTf Ph
PhOCH 2 CH O + H C PhCH O CO C H
2
2
2 2 5
OC H OH
2 5
98% e.e.
These catalysts function as Lewis acids at the carbonyl oxygen. The chiral ligands
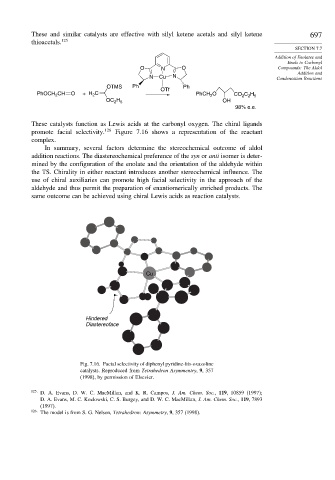
promote facial selectivity. 126 Figure 7.16 shows a representation of the reactant
complex.
In summary, several factors determine the stereochemical outcome of aldol
addition reactions. The diastereochemical preference of the syn or anti isomer is deter-
mined by the configuration of the enolate and the orientation of the aldehyde within
the TS. Chirality in either reactant introduces another stereochemical influence. The
use of chiral auxiliaries can promote high facial selectivity in the approach of the
aldehyde and thus permit the preparation of enantiomerically enriched products. The
same outcome can be achieved using chiral Lewis acids as reaction catalysts.
Cu
Hindered
Diastereoface
Fig. 7.16. Facial selectivity of diphenyl pyridine-bis-oxazoline
catalysts. Reproduced from Tetrahedron Asymmentry, 9, 357
(1998), by permission of Elsevier.
125 D. A. Evans, D. W. C. MacMillan, and K. R. Campos, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 119, 10859 (1997);
D. A. Evans, M. C. Kozlowski, C. S. Burgey, and D. W. C. MacMillan, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 119, 7893
(1997).
126
The model is from S. G. Nelson, Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 9, 357 (1998).