Page 711 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 711
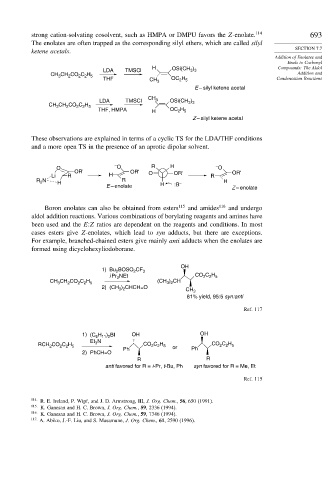
strong cation-solvating cosolvent, such as HMPA or DMPU favors the Z-enolate. 114 693
The enolates are often trapped as the corresponding silyl ethers, which are called silyl
SECTION 7.7
ketene acetals.
Addition of Enolates and
Enols to Carbonyl
H Compounds: The Aldol
LDA TMSCl OSi(CH 3 ) 3
CH CH CO C H Addition and
3
2
2 2 5
THF CH 3 OC H Condensation Reactions
2 5
E – silyl ketene acetal
CH
LDA TMSCl 3 OSi(CH )
3 3
CH CH CO C H
2 2 5
2
3
THF, HMPA H OC H
2 5
Z – silyl ketene acetal
These observations are explained in terms of a cyclic TS for the LDA/THF conditions
and a more open TS in the presence of an aprotic dipolar solvent.
– R H –
O O O
OR' OR' O OR' OR'
Li R H R
R N H R – H
2
E – enolate H :B Z – enolate
Boron enolates can also be obtained from esters 115 and amides 116 and undergo
aldol addition reactions. Various combinations of borylating reagents and amines have
been used and the E:Z ratios are dependent on the reagents and conditions. In most
cases esters give Z-enolates, which lead to syn adducts, but there are exceptions.
For example, branched-chained esters give mainly anti adducts when the enolates are
formed using dicyclohexyliodoborane.
OH
1) Bu BOSO CF 3
2
2
C H
i Pr NEt CO 2 2 5
2
CH CH CO C H (CH ) CH
2
3
2 2 5
3 2
2) (CH ) CHCH=O CH 3
3 2
81% yield, 95:5 syn:anti
Ref. 117
1) (C H ) BI OH OH
6 11 2
N
C H
Et 3
RCH CO C H CO 2 2 5 CO 2 2 5
C H
2 2 5
2
Ph or Ph
2) PhCH=O
R R
anti favored for R = i-Pr, t-Bu, Ph syn favored for R = Me, Et
Ref. 115
114
R. E. Ireland, P. Wipf, and J. D. Armstrong, III, J. Org. Chem., 56, 650 (1991).
115 K. Ganesan and H. C. Brown, J. Org. Chem., 59, 2336 (1994).
116 K. Ganesan and H. C. Brown, J. Org. Chem., 59, 7346 (1994).
117
A. Abiko, J.-F. Liu, and S. Masamune, J. Org. Chem., 61, 2590 (1996).