Page 770 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 770
753
– +
SECTION 8.5
Fused-Ring Systems
Azulene does have an appreciable dipole moment (0.8 D). 185 B3LYP/6-31G* and
MP2/6-31G* computations calculate the dipole moment as about 1.0 D. 184c d The essen-
tially single-bond nature of the shared bond indicates, however, that the conjugation
is principally around the periphery of the molecule.
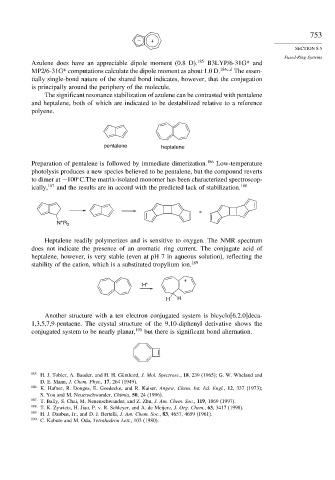
The significant resonance stabilization of azulene can be contrasted with pentalene
and heptalene, both of which are indicated to be destabilized relative to a reference
polyene.
pentalene heptalene
Preparation of pentalene is followed by immediate dimerization. 186 Low-temperature
photolysis produces a new species believed to be pentalene, but the compound reverts
to dimer at −100 C.The matrix-isolated monomer has been characterized spectroscop-
ically, 187 and the results are in accord with the predicted lack of stabilization. 188
+
+
N R 3
Heptalene readily polymerizes and is sensitive to oxygen. The NMR spectrum
does not indicate the presence of an aromatic ring current. The conjugate acid of
heptalene, however, is very stable (even at pH 7 in aqueous solution), reflecting the
stability of the cation, which is a substituted tropylium ion. 189
+
H +
H H
Another structure with a ten electron conjugated system is bicyclo[6.2.0]deca-
1,3,5,7,9-pentaene. The crystal structure of the 9,10-diphenyl derivative shows the
conjugated system to be nearly planar, 190 but there is significant bond alternation.
185
H. J. Tobler, A. Bauder, and H. H. Günthard, J. Mol. Spectrosc., 18, 239 (1965); G. W. Wheland and
D. E. Mann, J. Chem. Phys., 17, 264 (1949).
186 K. Hafner, R. Donges, E. Goedecke, and R. Kaiser, Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 12, 337 (1973);
S. You and M. Neuenschwander, Chimia, 50, 24 (1996).
187
T. Bally, S. Chai, M. Neuenschwander, and Z. Zhu, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 119, 1869 (1997).
188
T. K. Zywietz, H. Jiao, P. v. R. Schleyer, and A. de Meijere, J. Org. Chem., 63, 3417 (1998).
189 H. J. Dauben, Jr., and D. J. Bertelli, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 83, 4657, 4659 (1961).
190
C. Kabuto and M. Oda, Tetrahedron Lett., 103 (1980).