Page 149 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 149
Scheme 2.6. (Continued) 121
9 i SECTION 2.1
S O OTBDPS OH OTBDPS
S O Aldol Addition and
O CH Condensation Reactions
S N O Sn(OTf) 2
+ i Pr NEt S N O
O 2 O
CH 2 OCH 2 Ph CH 3
CH(CH 3 ) 2 CH 2 OCH 2 Ph
–78°C
CH(CH 3 ) 2
96%
a. S. F. Martin and D. E. Guinn, J. Org. Chem., 52, 5588 (1987).
b. D. Seebach, H.-F. Chow, R. F. W. Jackson, K. Lawson, M. A. Sutter, S. Thaisrivongs, and J. Zimmerman, J. Am.
Chem. Soc., 107, 5292 (1985).
c. S. J. Mickel, G. H. Sedelmeier, D. Niererer, R. Daeffler, A. Osmani, K. Schreiner, M. Seeger-Weibel, B. Berod,
K. Schaer, R. Gamboni, S. Chen, W. Chen, C. T. Jagoe, F. Kinder, M. Low, K. Prasad, O. Repic, W. C. Shieh,
R. M. Wang, L. Wakole, D. Xu, and S. Xue, Org. Proc. Res. Dev., 8, 92 (2004).
d. D. A. Evans, J. S. Clark, R. Metternich, V. J. Novack, and G. S. Sheppard, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 112, 866 (1990).
e. G. E. Keck and G. D. Lundquist, J. Org. Chem., 64, 4482 (1999).
f. L. C. Dias, L. G. de Oliveira, and M. A. De Sousa, Org. Lett., 5, 265 (2003).
g. M. T. Crimmins and J. She, Synlett, 1371 (2004).
h. J. Wu, X. Shen, Y.-Q. Yang, Q. Hu, and J.-H. Huang, J. Org. Chem., 69, 3857 (2004).
i. D. Zuev and L. A. Paquette, Org. Lett., 2, 679 (2000).
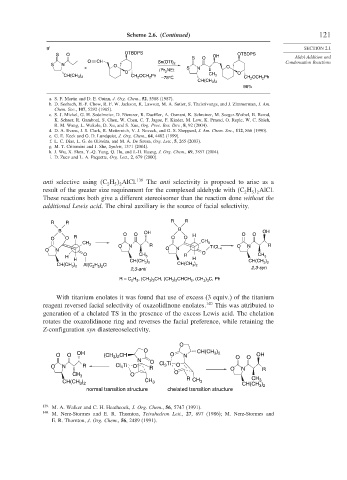
anti selective using C H AlCl. 139 The anti selectivity is proposed to arise as a
2
5 2
result of the greater size requirement for the complexed aldehyde with C H AlCl.
2
5 2
These reactions both give a different stereoisomer than the reaction done without the
additional Lewis acid. The chiral auxiliary is the source of facial selectivity.
R R R R
B OH B OH
O O H O O
O O R O O
CH CH 3
3 R R
O N TiCL O N
O N O N 4
O R O
H CH 3 CH 3
H CH(CH ) H CH(CH )
CH(CH ) Al(C H ) Cl 3 2 CH(CH ) 3 2
3 2
3 2
5 2
2
2,3-anti 2,3-syn
R = C H , (CH ) CH, (CH ) CHCH , (CH ) C, Ph
2 5 3 3 3 2 2 3 3
With titanium enolates it was found that use of excess (3 equiv.) of the titanium
reagent reversed facial selectivity of oxazolidinone enolates. 140 This was attributed to
generation of a chelated TS in the presence of the excess Lewis acid. The chelation
rotates the oxazolidinone ring and reverses the facial preference, while retaining the
Z-configuration syn diastereoselectivity.
O
O CH(CH )
O O OH (CH 3 2 O N 3 2 O O OH
) CH
N O
3
O N R Cl Ti O R Cl Ti O O N R
4
O O
CH 3
) CH 3 R CH 3 CH 3
CH(CH 3 2 )
CH(CH 3 2
normal transition structure chelated transition structure
139 M. A. Walker and C. H. Heathcock, J. Org. Chem., 56, 5747 (1991).
140
M. Nerz-Stormes and E. R. Thornton, Tetrahedron Lett., 27, 897 (1986); M. Nerz-Stormes and
E. R. Thornton, J. Org. Chem., 56, 2489 (1991).