Page 234 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 234
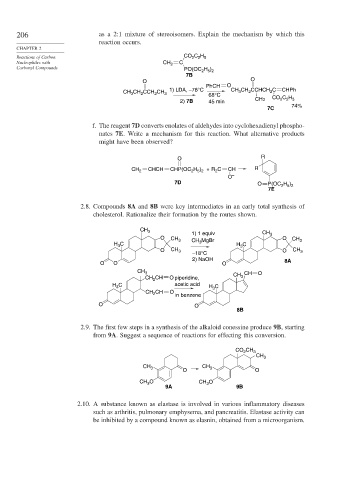
206 as a 2:1 mixture of stereoisomers. Explain the mechanism by which this
reaction occurs.
CHAPTER 2
Reactions of Carbon CO C H
2 2 5
Nucleophiles with CH 2 C
Carbonyl Compounds H )
PO(OC 2 5 2
7B
O O
PhCH O
1) LDA, –78°C CH CH CCHCH C CHPh
CH CH CCH CH 3 68°C 3 2 2
3
2
2
2 2 5
2) 7B 45 min CH3 CO C H
74%
7C
f. The reagent 7D converts enolates of aldehydes into cyclohexadienyl phospho-
nates 7E. Write a mechanism for this reaction. What alternative products
might have been observed?
O R
CH 2 CHCH CHP(OC H ) + R C CH R
2 5 2
2
O –
7D O P(OC H )
2 5 2
7E
2.8. Compounds 8A and 8B were key intermediates in an early total synthesis of
cholesterol. Rationalize their formation by the routes shown.
CH 3 CH
1) 1 equiv 3
O CH 3 MgBr O CH 3
H C CH 3 H 3 C
3
O CH 3 O CH 3
–18°C
2) NaOH 8A
O O O
CH 3 CH O
CH O piperidine, CH 3
CH 2
H C acetic acid H C
3
3
CH CH O in benzene
2
O O
8B
2.9. The first few steps in a synthesis of the alkaloid conessine produce 9B, starting
from 9A. Suggest a sequence of reactions for effecting this conversion.
CO 2 CH 3
CH 3
CH 3 CH 3
O O
CH O CH O
3
3
9A 9B
2.10. A substance known as elastase is involved in various inflammatory diseases
such as arthritis, pulmonary emphysema, and pancreatitis. Elastase activity can
be inhibited by a compound known as elasnin, obtained from a microorganism.