Page 847 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part B - Reactions & Synthesis
P. 847
823
F
(a) Me Sr· O H
F F Me Me SECTION 9.2
Sr· O Me O H Organosilicon
F H F H Compounds
O H H
F H Me
H
Me
C(3)-C(4) are eclipsed
C(3)
C(4)
2.29 Å 2.26 Å
2.17 Å
(b) Me
Me F O
F O Me Me F
Me F O O S
H O S
Me H H H F
O F
H H Me H
Me H
Me
Me
2.34 Å 2.31 Å
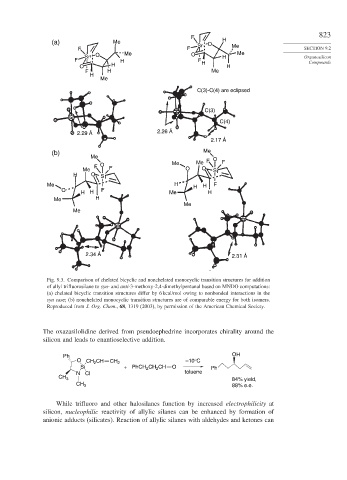
Fig. 9.3. Comparison of chelated bicyclic and nonchelated monocyclic transition structures for addition
of allyl trifluorosilane to syn- and anti-3-methoxy-2,4-dimethylpentanal based on MNDO computations:
(a) chelated bicyclic transition structures differ by 6 kcal/mol owing to nonbonded interactions in the
syn case; (b) nonchelated monocyclic transition structures are of comparable energy for both isomers.
Reproduced from J. Org. Chem., 68, 1319 (2003), by permission of the American Chemical Society.
The oxazasilolidine derived from pseudoephedrine incorporates chirality around the
silicon and leads to enantioselective addition.
Ph OH
O CH CH CH –10°C
2 2
Si + PhCH CH CH O Ph
2
2
N Cl toluene
84% yield,
CH 3
CH 3 88% e.e.
While trifluoro and other halosilanes function by increased electrophilicity at
silicon, nucleophilic reactivity of allylic silanes can be enhanced by formation of
anionic adducts (silicates). Reaction of allylic silanes with aldehydes and ketones can