Page 108 - Advances in Biomechanics and Tissue Regeneration
P. 108
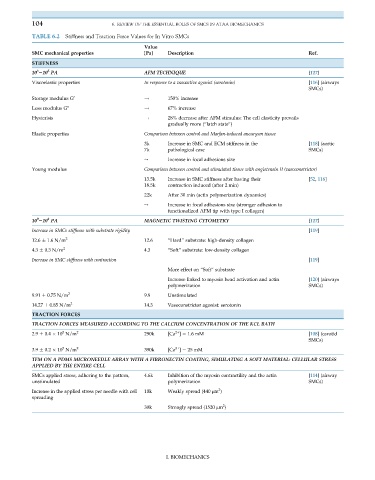
104 6. REVIEW OF THE ESSENTIAL ROLES OF SMCS IN ATAA BIOMECHANICS
TABLE 6.2 Stiffness and Traction Force Values for In Vitro SMCs
Value
SMC mechanical properties [Pa] Description Ref.
STIFFNESS
5
3
10 210 PA AFM TECHNIQUE [117]
Viscoelastic properties In response to a vasoactive agonist (serotonin) [116] (airways
SMCs)
Storage modulus G 0 ! 150% increase
Loss modulus G 00 ! 67% increase
Hysterisis ! 28% decrease after AFM stimulus: The cell elasticity prevails
gradually more (“latch state”)
Elastic properties Comparison between control and Marfan-induced aneurysm tissue
3k Increase in SMC and ECM stiffness in the [118] (aortic
7k pathological case SMCs)
↪ Increase in focal adhesions size
Young modulus Comparison between control and stimulated tissue with angiotensin II (vasoconstrictor)
13.5k Increase in SMC stiffness after having their [52, 116]
18.5k contraction induced (after 2 min)
22k After 30 min (actin polymerization dynamics)
↪ Increase in focal adhesions size (stronger adhesion to
functionalized AFM tip with type I collagen)
0
2
10 210 PA MAGNETIC TWISTING CYTOMETRY [117]
Increase in SMCs stiffness with substrate rigidity [119]
12.6 1.6 N/m 2 12.6 “Hard” substrate: high-density collagen
4.3 0.3 N/m 2 4.3 “Soft” substrate: low-density collagen
Increase in SMC stiffness with contraction [119]
More effect on “Soft” substrate
Increase linked to myosin head activation and actin [120] (airways
polymerization SMCs)
9.91 0.75 N/m 2 9.9 Unstimulated
14.27 0.85 N/m 2 14.3 Vasoconstrictor agonist: serotonin
TRACTION FORCES
TRACTION FORCES MEASURED ACCORDING TO THE CALCIUM CONCENTRATION OF THE KCL BATH
2+
5
2.9 0.4 10 N/m 2 290k [Ca ] ¼ 1.6 mM [108] (carotid
SMCs)
2+
5
3.9 0.2 10 N/m 2 390k [Ca ] ¼ 25 mM
TFM ON A PDMS MICRONEEDLE ARRAY WITH A FIBRONECTIN COATING, SIMULATING A SOFT MATERIAL: CELLULAR STRESS
APPLIED BY THE ENTIRE CELL
SMCs applied stress, adhering to the pattern, 4.6k Inhibition of the myosin contractility and the actin [114] (airway
unstimulated polymerization SMCs)
2
Increase in the applied stress per needle with cell 10k Weakly spread (440 μm )
spreading
2
30k Strongly spread (1520 μm )
I. BIOMECHANICS