Page 428 - Aircraft Stuctures for Engineering Student
P. 428
10.4 Fuselage frames and wing ribs 409
10325 N
2825 N
Tension
6.7 - 11.3 - D
A 23.3
Shear flows in Wrnm
- G 2.6 ,,
23.3
6.7
F
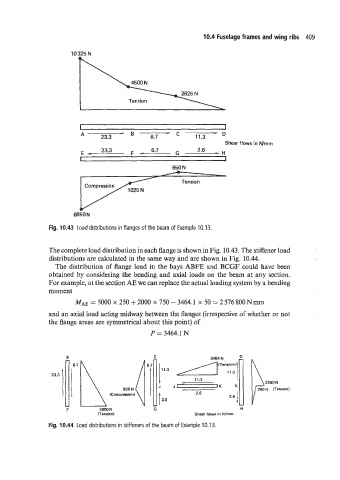
Fig. 10.43 Load distributions in flanges of the beam of Example 10.13.
The complete load distribution in each flange is shown in Fig. 10.43. The stiffener load
distributions are calculated in the same way and are shown in Fig. 10.44.
The distribution of flange load in the bays ABFE and BCGF could have been
obtained by considering the bending and axial loads on the beam at any section.
For example, at the section AE we can replace the actual loading system by a bending
moment
MAE = 5000 x 250 + 2000 x 750 - 3464.1 x 50 = 2 576 800 N IIUII
and an axial load acting midway between the flanges (irrespective of whether or not
the flange areas are symmetrical about this point) of
P = 3464.1 N
3464 N
6.7
11.3
2260 N
J J r K K
2.6
E H
(Tension) Shear flows in Nlmm
Fig. 10.44 Load distributions in stiffeners of the beam of Example 10.13.