Page 198 - APPLIED PROCESS DESIGN FOR CHEMICAL AND PETROCHEMICAL PLANTS, Volume 1, 3rd Edition
P. 198
Pumping of Liquids 171
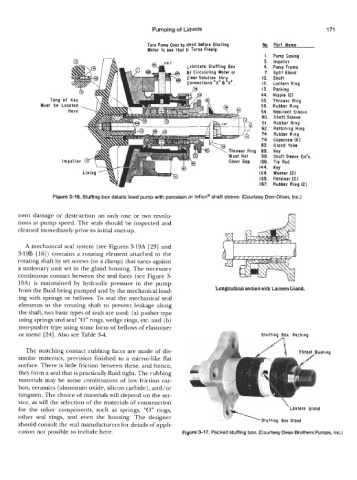
Turn Pump Over by Hand before Starting No.
- Part Name
Motor to see that It Turns Freely.
I. Pump Casing
.xay 3. Impeller
Lubricate Stuffina Box 4. Pump Frame
BY Circulating Waier or 7. Split Gland
Clear Solution thr; ~ IO. Shaft
Connections “x” a Y . 12. Lontern Ring
13. Packing
44. Nipple (2)
Tang 55. Thrower Ring
Must be 56. Rubber Ring
5 9.
~ .. Resilient Sleeve
60. Shaft Sleeve
61. Rubber Ring
^^
Retaining Ring
Rubber Ring
Capscrew (6)
Gland Yoke
Key
Shaft Sleeve Ext’n.
Impeller Tie Rod
Key
Lining 164. Washer (2)
165. Retainer (2)
167. Rubber Ring (2)
Figure 3-16. Stuffing box details lined pump with porcelain or teflon@ shaft sleeve. (Courtesy Dorr-Oliver, Inc.)
nent damage or destruction on only one or two revolu-
tions at pump speed. The seals should be inspected and
cleaned immediately prior to initial start-up.
A mechanical seal system (see Figures 3-19A [23] and
3-19B [16]) contains a rotating element attached to the
rotating shaft by set screws (or a clamp) that turns against
a stationary unit set in the gland housing. The necessary
continuous contact between the seal faces (see Figure 3-
19A) is maintained by hydraulic pressure in the pump ba
from the fluid being pumped and by the mechanical load- Longitudinal sectionwith Lantern Gland.
ing with springs or bellows. To seal the mechanical seal
elements to the rotating shaft to prevent leakage along
the shaft, two basic types of seals are used: (a) pusher type
using springs and seal “0” rings, wedge rings, etc. and (b)
non-pusher type using some form of bellows of elastomer
or metal [24]. Also see Table 3-4.
The matching contact rubbing faces are made of dis-
similar materials, precision finished to a mirror-like flat
surface. There is little friction between these, and hence,
they form a seal that is practically fluid tight. The rubbing
materials may be some combination of low friction car-
bon, ceramics (aluminum oxide, silicon carbide), and/or
tungsten. The choice of materials will depend on the ser-
vice, as will the selection of the materials of construction
for the other components, such as springs, “0” rings, ‘Lantern Gland
other seal rings, and even the housing. The designer
should consult the seal manufacturers for details of appli- Stuffing Box Gland
cation not possible to include here. Figure 3-17. Packed stuffing box. (Courtesy Dean Brothers Pumps, Inc.)