Page 105 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 105
3.5 LOW-OXIDATION-STATE COMPOUNDS 85
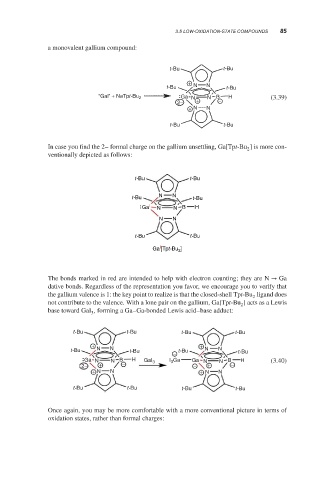
a monovalent gallium compound:
t-Bu t-Bu
+
t-Bu N N t-Bu
“Gal” + NaTpt-Bu 2 Ga N N B H (3.39)
2− + −
+ N N
t-Bu t-Bu
In case you find the 2– formal charge on the gallium unsettling, Ga[Tpt-Bu ] is more con-
2
ventionally depicted as follows:
t-Bu t-Bu
t-Bu N N t-Bu
Ga I N N B H
N N
t-Bu t-Bu
I
Ga [Tpt-Bu 2 ]
The bonds marked in red are intended to help with electron counting; they are N → Ga
dative bonds. Regardless of the representation you favor, we encourage you to verify that
the gallium valence is 1: the key point to realize is that the closed-shell Tpt-Bu ligand does
2
not contribute to the valence. With a lone pair on the gallium, Ga[Tpt-Bu ] acts as a Lewis
2
base toward GaI , forming a Ga–Ga-bonded Lewis acid–base adduct:
3
t-Bu t-Bu t-Bu t-Bu
+ +
t-Bu N N t-Bu t-Bu N N t-Bu
−
Ga N N B H GaI 3 I 3 Ga Ga N N B H (3.40)
2− + − − + −
+ N N + N N
t-Bu t-Bu t-Bu t-Bu
Once again, you may be more comfortable with a more conventional picture in terms of
oxidation states, rather than formal charges: