Page 126 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 126
GROUP 14 ELEMENTS
106
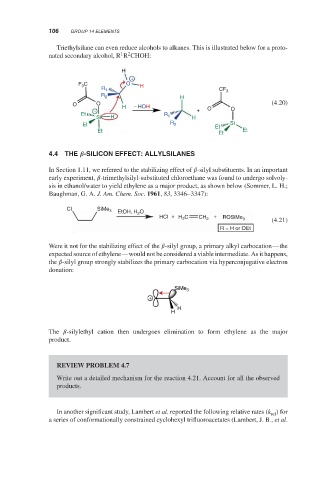
Triethylsilane can even reduce alcohols to alkanes. This is illustrated below for a proto-
1 2
nated secondary alcohol, R R CHOH:
H
+
F C O H
3
R 1 CF 3
R 2 H
O O H − HOH (4.20)
− + O O
Et R
Si H 1 H
Et R 2 Et Si
Et Et Et
THE -SILICON EFFECT: ALLYLSILANES
4.4
In Section 1.11, we referred to the stabilizing effect of -silyl substituents. In an important
early experiment, -trimethylsilyl-substituted chloroethane was found to undergo solvoly-
sis in ethanol/water to yield ethylene as a major product, as shown below (Sommer, L. H.;
Baughman, G. A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1961, 83, 3346–3347):
Cl SiMe 3 EtOH, H 2 O
HCl + H 2 C CH 2 + ROSiMe 3 (4.21)
R = H or OEt
Were it not for the stabilizing effect of the -silyl group, a primary alkyl carbocation—the
expected source of ethylene—would not be considered a viable intermediate. As it happens,
the -silyl group strongly stabilizes the primary carbocation via hyperconjugative electron
donation:
SiMe 3
+
H
H
The -silylethyl cation then undergoes elimination to form ethylene as the major
product.
REVIEW PROBLEM 4.7
Write out a detailed mechanism for the reaction 4.21. Account for all the observed
products.
In another significant study, Lambert et al. reported the following relative rates (k )for
rel
a series of conformationally constrained cyclohexyl trifluoroacetates (Lambert, J. B., et al.