Page 199 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 199
5B.9 THE WITTIG AND RELATED REACTIONS: PHOSPHORUS YLIDES 179
REVIEW PROBLEM 5B.15
With respect to the catalytic Wittig reaction discussed above, draw a mechanism for
the reduction of the phosphine oxide R PO by the silane Ph SiH .
3 2 2
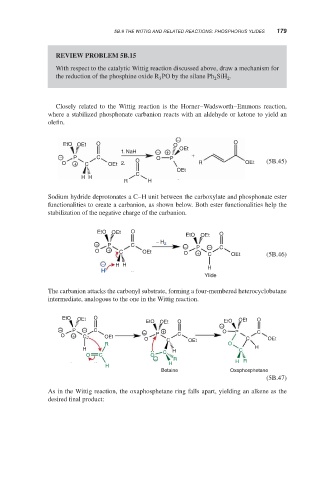
Closely related to the Wittig reaction is the Horner–Wadsworth–Emmons reaction,
where a stabilized phosphonate carbanion reacts with an aldehyde or ketone to yield an
olefin.
−
EtO OEt O O O
1. NaH − + OEt
− P C O P +
O + C OEt 2. O R OEt (5B.45)
OEt
C
HH
R H
Sodium hydride deprotonates a C–H unit between the carboxylate and phosphonate ester
functionalities to create a carbanion, as shown below. Both ester functionalities help the
stabilization of the negative charge of the carbanion.
EtO OEt O
EtO OEt O
− P C − H 2 − −
O + C OEt O P C C OEt (5B.46)
+
− H H
H H
Ylide
The carbanion attacks the carbonyl substrate, forming a four-membered heterocyclobutane
intermediate, analogous to the one in the Wittig reaction.
EtO OEt O OEt O
EtO OEt O EtO
− P − C − + − O P C
O + C OEt P C
O C OEt C OEt
R O
H C H
C H
O C O
− R R
H H
H
Betaine Oxaphosphetane
(5B.47)
As in the Wittig reaction, the oxaphosphetane ring falls apart, yielding an alkene as the
desired final product: