Page 203 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 203
5B.10 PHOSPHAZENES 183
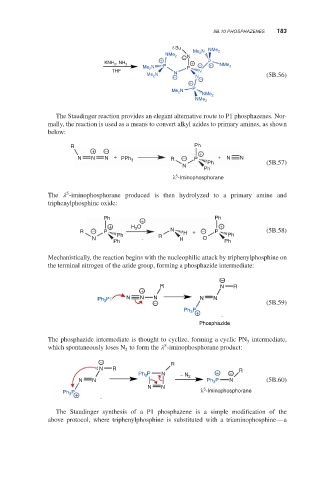
t-Bu NMe
Me 2 N 2
NMe 2 N
+ − P
, NH
3 P − + NMe 2
KNH 2 +
Me N P
THF 2 N
Me 2 N N (5B.56)
− N −
+
P
N
Me 2
NMe 2
NMe 2
The Staudinger reaction provides an elegant alternative route to P1 phosphazenes. Nor-
mally, the reaction is used as a means to convert alkyl azides to primary amines, as shown
below:
R Ph
+ − +
N N N + PPh 3 R − P + N N
Ph (5B.57)
N
Ph
5
λ -Iminophosphorane
5
The -iminophosphorane produced is then hydrolyzed to a primary amine and
triphenylphosphine oxide:
Ph + Ph
+ H 3 O +
R − P N H + − P (5B.58)
Ph R Ph
N H O
Ph Ph
Mechanistically, the reaction begins with the nucleophilic attack by triphenylphosphine on
the terminal nitrogen of the azide group, forming a phosphazide intermediate:
−
R N R
+
P N N N N N
− (5B.59)
Ph 3
Ph 3 P +
Phosphazide
The phosphazide intermediate is thought to cyclize, forming a cyclic PN intermediate,
3
5
which spontaneously loses N to form the -iminophosphorane product:
2
− R
N R R
P N + −
Ph 3
− N 2
N N Ph P N (5B.60)
3
N N 5
Ph 3 P + λ -Iminophosphorane
The Staudinger synthesis of a P1 phosphazene is a simple modification of the
above protocol, where triphenylphosphine is substituted with a triaminophosphine—a