Page 47 - Arrow Pushing in Inorganic Chemistry A Logical Approach to the Chemistry of the Main Group Elements
P. 47
1.15 CARBANIONS AND RELATED SYNTHETIC INTERMEDIATES 27
The best known among unstabilized carbanionic derivatives are the Grignard reagents
(organomagnesium compounds) and organolithiums:
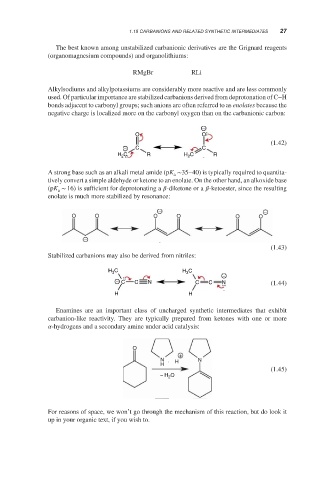
RMgBr RLi
Alkylsodiums and alkylpotassiums are considerably more reactive and are less commonly
used. Of particular importance are stabilized carbanions derived from deprotonation of C–H
bonds adjacent to carbonyl groups; such anions are often referred to as enolates because the
negative charge is localized more on the carbonyl oxygen than on the carbanionic carbon:
−
O O
(1.42)
− C C
H C R H C R
2
2
A strong base such as an alkali metal amide (pK ∼35–40) is typically required to quantita-
a
tively convert a simple aldehyde or ketone to an enolate. On the other hand, an alkoxide base
(pK ∼ 16) is sufficient for deprotonating a -diketone or a -ketoester, since the resulting
a
enolate is much more stabilized by resonance:
− −
O O O O O O
−
(1.43)
Stabilized carbanions may also be derived from nitriles:
H C H C
3
3
−
− C C N C C N (1.44)
H H
Enamines are an important class of uncharged synthetic intermediates that exhibit
carbanion-like reactivity. They are typically prepared from ketones with one or more
-hydrogens and a secondary amine under acid catalysis:
O
+
N , H N
H
(1.45)
− H 2 O
For reasons of space, we won’t go through the mechanism of this reaction, but do look it
up in your organic text, if you wish to.