Page 270 - Automotive Engineering Powertrain Chassis System and Vehicle Body
P. 270
CH AP TER 9 .1 Steering
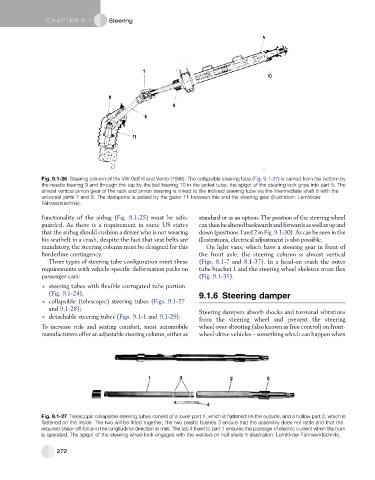
Fig. 9.1-26 Steering column of the VW Golf III and Vento (1996). The collapsible steering tube (Fig. 9.1-27) is carried from the bottom by
the needle bearing 9 and through the top by the ball bearing 10 in the jacket tube; the spigot of the steering lock grips into part 5. The
almost vertical pinion gear of the rack and pinion steering is linked to the inclined steering tube via the intermediate shaft 6 with the
universal joints 7 and 8. The dashpanel is sealed by the gaiter 11 between this and the steering gear (illustration: Lemfo ¨ rder
Fahrwerktechnik).
functionality of the airbag (Fig. 9.1-25) must be safe- standard or as an option. The position of the steering wheel
guarded. As there is a requirement in some US states canthenbealteredbackwardsandforwardsaswellasupand
that the airbag should cushion a driver who is not wearing down (positions 1 and 2 in Fig. 9.1-30). As can be seen in the
his seatbelt in a crash, despite the fact that seat belts are illustrations, electrical adjustment is also possible.
mandatory, the steering column must be designed for this On light vans, which have a steering gear in front of
borderline contingency. the front axle, the steering column is almost vertical
Three types of steering tube configuration meet these (Figs. 8.1-7 and 8.1-37). In a head-on crash the outer
requirements with vehicle-specific deformation paths on tube bracket 1 and the steering wheel skeleton must flex
passenger cars: (Fig. 9.1-31).
steering tubes with flexible corrugated tube portion
(Fig. 9.1-24); 9.1.6 Steering damper
collapsible (telescopic) steering tubes (Figs. 9.1-27
and 9.1-28); Steering dampers absorb shocks and torsional vibrations
detachable steering tubes (Figs. 9.1-1 and 9.1-29).
from the steering wheel and prevent the steering
To increase ride and seating comfort, most automobile wheel over-shooting (also known as free control) on front-
manufacturers offer an adjustable steering column, either as wheel-drive vehicles – something which can happen when
Fig. 9.1-27 Telescopic collapsible steering tubes consist of a lower part 1, which is flattened on the outside, and a hollow part 2, which is
flattened on the inside. The two will be fitted together; the two plastic bushes 3 ensure that the assembly does not rattle and that the
required shear-off force in the longitudinal direction is met. The tab 4 fixed to part 1 ensures the passage of electric current when the horn
is operated. The spigot of the steering wheel lock engages with the welded-on half shells 5 (illustration: Lemfo ¨ rder Fahrwerktechnik).
272