Page 244 - Battery Reference Book
P. 244
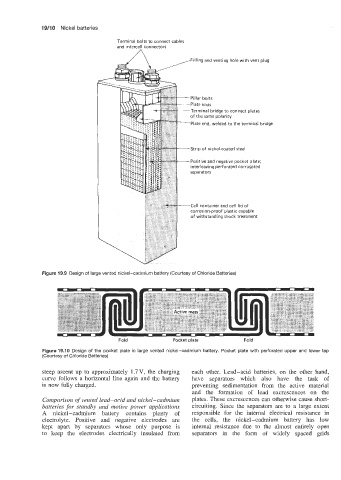
19/10 Nickel batteries
Terminal bolts to connect cables
and intercell connectors
,Filling and venting hole with vent plug
Strip of nickel-coated steel
Positive and negative pocket plate,
interleaving perforated corrugated
separators
Cell container and cell lid of
corrosion-proof plastic capable
of withstanding shock treatment
Figure 19.9 Design of large vented nickel-cadmium battery (Courtesy of Chloride Batteries)
Fold Pocket plate Fold
Figure 19.10 Design of the pocket plate in large vented nickel-cadmium battery. Pocket plate with perforated upper and lower tap
(Courtesy of Chloride Batteries)
steep ascent up to approximately 1.7 V, the charging each other. Lead-acid batteries, on the other hand,
curve follows a horizontal line again and the battery have separators which also have the task of
is now fully charged. preventing sedimentation from the active material
and the formation of lead excrescences on the
Comparison of vented lead-acid and nickel-cadmium plates. These excrescences can otherwise cause short-
batteries for standby and motive power applications circuiting. Since the separators are to a large extent
A nickel-cadmium battery contains plenty of responsible for the internal electrical resistance in
electrolyte. Positive and negative electrodes are the cells, the nickel-cadmium battery has low
kept apart by separators whose only purpose is internal resistance due to the almost entirely open
to keep the electrodes electrically insulated from separators in the form of widely spaced grids