Page 167 - Bebop to The Boolean Boogie An Unconventional Guide to Electronics Fundamentals, Components, and Processes
P. 167
148 rn Chapter Fourteen
Gas containinq The remaining silicon
dioxide layer is removed
by means of an appropri-
ate solvent that doesn’t
affect the silicon sub-
strate (including the
doped regions). Then
additional masks and
variations on the process
are used to create two
(substrate)
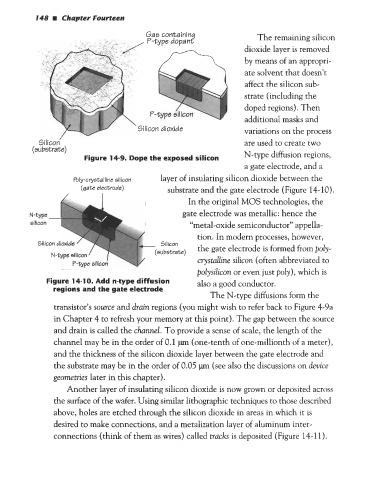
Figure 14-9. Dope the exposed silicon N-type diffusion regions,
a gate electrode, and a
Poly-crystalline silicon layer of insulating silicon dioxide between the
(gate electrode) substrate and the gate electrode (Figure 14-10).
/ I
In the original MOS technologies, the
gate electrode was metallic: hence the
“metal-oxide semiconductor” appella-
tion. In modern processes, however,
- Silicon
(substrate) the gate electrode is formed from poly-
crystalline silicon (often abbreviated to
polysilicon or even just poly), which is
Figure 14-1 0. Add n-type diffusion also a good conductor.
regions and the gate electrode
The N-type diffusions form the
transistor’s source and drain regions (you might wish to refer back to Figure 4-9a
in Chapter 4 to refresh your memory at this point). The gap between the source
and drain is called the channel. To provide a sense of scale, the length of the
channel may be in the order of 0.1 pm (one-tenth of one-millionth of a meter),
and the thickness of the silicon dioxide layer between the gate electrode and
the substrate may be in the order of 0.05 pm (see also the discussions on dewice
geometries later in this chapter).
Another layer of insulating silicon dioxide is now grown or deposited across
the surface of the wafer. Using similar lithographic techniques to those described
above, holes are etched through the silicon dioxide in areas in which it is
desired to make connections, and a metalization layer of aluminum inter-
connections (think of them as wires) called tracks is deposited (Figure 14-1 1).