Page 349 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 349
15.2 Cascade Reactions for Assaying Transketolase Activity In Vitro 325
clinical monitoring and biomedical research such as the screening of TK inhibitors
proposed for the treatment of many diseases.
Although very sensitive, the multienzymatic cascade assays described so far
to quantify the activity of wild-type or modified TK catalysts suffer from several
limitations, such as the setting-up of coupling enzymatic reactions that require the
extra preparation of noncommercial auxiliary enzymes or the multistep synthesis
of specialized TK probes that prevents their use for the measurement of a large
number of samples, such as for the screening of TK libraries. In addition, the general
requirement of specific natural donor/acceptor substrates is not compatible with
the determination of nonnatural substrate analogs. In the course of modifying TK
by directed mutagenesis, rapid, easy, and inexpensive assays have recently been
developed. These assays involve a nonprotein auxiliary agent introduced to the
reaction mixture, thereby enabling a colorimetric assay.
15.2.2
Coupling with a Nonprotein Auxiliary Agent
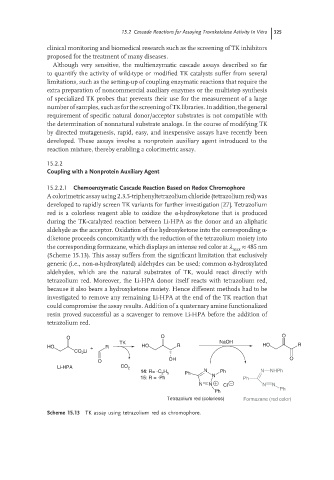
15.2.2.1 Chemoenzymatic Cascade Reaction Based on Redox Chromophore
A colorimetric assay using 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (tetrazolium red) was
developed to rapidly screen TK variants for further investigation [27]. Tetrazolium
red is a colorless reagent able to oxidize the α-hydroxyketone that is produced
during the TK-catalyzed reaction between Li-HPA as the donor and an aliphatic
aldehyde as the acceptor. Oxidation of the hydroxyketone into the corresponding α-
diketone proceeds concomitantly with the reduction of the tetrazolium moiety into
the corresponding formazane, which displays an intense red color at ≈ 485 nm
max
(Scheme 15.13). This assay suffers from the significant limitation that exclusively
generic (i.e., non-α-hydroxylated) aldehydes can be used; common α-hydroxylated
aldehydes, which are the natural substrates of TK, would react directly with
tetrazolium red. Moreover, the Li-HPA donor itself reacts with tetrazolium red,
because it also bears a hydroxyketone moiety. Hence different methods had to be
investigated to remove any remaining Li-HPA at the end of the TK reaction that
could compromise the assay results. Addition of a quaternary amine functionalized
resin proved successful as a scavenger to remove Li-HPA before the addition of
tetrazolium red.
O O O
TK NaOH
HO + R HO R HO R
Li
CO 2
OH O
O
Li-HPA CO 2
14: R= -C H 5 Ph N Ph N NHPh
2
15: R = -Ph N Ph
N N Cl N N
Ph Ph
Tetrazolium red (colorless) Formazane (red color)
Scheme 15.13 TK assay using tetrazolium red as chromophore.