Page 347 - Cascade_Biocatalysis_Integrating_Stereoselective_and_Environmentally_Friendly_Reactions
P. 347
15.2 Cascade Reactions for Assaying Transketolase Activity In Vitro 323
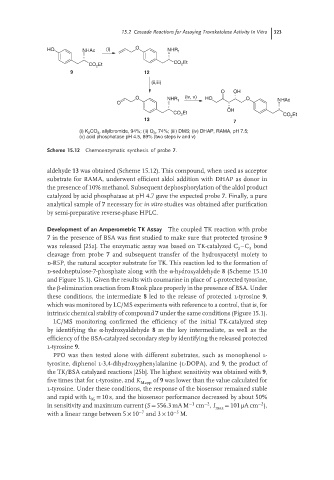
HO NHAc (i) O NHR 1
CO Et
Et 2
CO 2
9 12
(ii,iii)
O OH
O NHR (iv, v) HO O NHAc
O 1
OH
Et
CO 2 Et
CO 2
13
7
(i) K 2 CO 3 , allylbromide, 94%; (ii) O 3 , 74%; (iii) DMS; (iv) DHAP, RAMA, pH 7.5;
(v) acid phosphatase pH 4.5, 89% (two steps iv and v)
Scheme 15.12 Chemoenzymatic synthesis of probe 7.
aldehyde 13 was obtained (Scheme 15.12). This compound, when used as acceptor
substrate for RAMA, underwent efficient aldol addition with DHAP as donor in
the presence of 10% methanol. Subsequent dephosphorylation of the aldol product
catalyzed by acid phosphatase at pH 4.7 gave the expected probe 7.Finally,apure
analytical sample of 7 necessary for in vitro studies was obtained after purification
by semi-preparative reverse-phase HPLC.
Development of an Amperometric TK Assay The coupled TK reaction with probe
7 in the presence of BSA was first studied to make sure that protected tyrosine 9
was released [25a]. The enzymatic assay was based on TK-catalyzed C –C bond
2 3
cleavage from probe 7 and subsequent transfer of the hydroxyacetyl moiety to
d-R5P, the natural acceptor substrate for TK. This reaction led to the formation of
d-sedoheptulose-7-phosphate along with the α-hydroxyaldehyde 8 (Scheme 15.10
and Figure 15.1). Given the results with coumarine in place of l-protected tyrosine,
the β-elimination reaction from 8 took place properly in the presence of BSA. Under
these conditions, the intermediate 8 led to the release of protected l-tyrosine 9,
which was monitored by LC/MS experiments with reference to a control, that is, for
intrinsic chemical stability of compound 7 under the same conditions (Figure 15.1).
LC/MS monitoring confirmed the efficiency of the initial TK-catalyzed step
by identifying the α-hydroxyaldehyde 8 as the key intermediate, as well as the
efficiency of the BSA-catalyzed secondary step by identifying the released protected
l-tyrosine 9.
PPO was then tested alone with different substrates, such as monophenol l-
tyrosine, diphenol l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (l-DOPA), and 9,the productof
the TK/BSA catalyzed reactions [25b]. The highest sensitivity was obtained with 9,
five times that for l-tyrosine, and K of 9 was lower than the value calculated for
Mapp
l-tyrosine. Under these conditions, the response of the biosensor remained stable
and rapid with t = 10 s, and the biosensor performance decreased by about 50%
95
−2
−2
in sensitivity and maximum current (S = 556.3 mA M −1 cm , I = 101 μAcm ),
max
with a linear range between 5 × 10 −7 and 3 × 10 −5 M.