Page 394 - Boiler_Operators_Handbook,_Second_Edition
P. 394
Controls 379
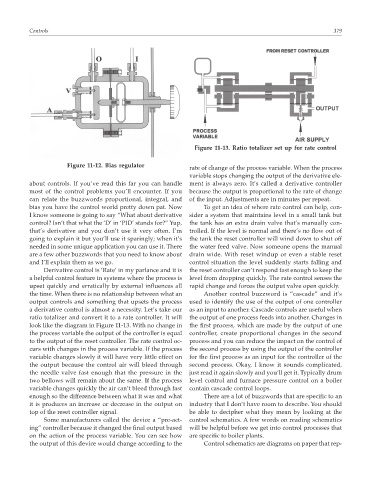
Figure 11-13. Ratio totalizer set up for rate control
Figure 11-12. Bias regulator
rate of change of the process variable. When the process
variable stops changing the output of the derivative ele-
about controls. If you’ve read this far you can handle ment is always zero. It’s called a derivative controller
most of the control problems you’ll encounter. If you because the output is proportional to the rate of change
can relate the buzzwords proportional, integral, and of the input. Adjustments are in minutes per repeat.
bias you have the control world pretty down pat. Now To get an idea of where rate control can help, con-
I know someone is going to say “What about derivative sider a system that maintains level in a small tank but
control? Isn’t that what the ‘D’ in ‘PID’ stands for?” Yup, the tank has an extra drain valve that’s manually con-
that’s derivative and you don’t use it very often. I’m trolled. If the level is normal and there’s no flow out of
going to explain it but you’ll use it sparingly; when it’s the tank the reset controller will wind down to shut off
needed in some unique application you can use it. There the water feed valve. Now someone opens the manual
are a few other buzzwords that you need to know about drain wide. With reset windup or even a stable reset
and I’ll explain them as we go. control situation the level suddenly starts falling and
Derivative control is ‘Rate’ in my parlance and it is the reset controller can’t respond fast enough to keep the
a helpful control feature in systems where the process is level from dropping quickly. The rate control senses the
upset quickly and erratically by external influences all rapid change and forces the output valve open quickly.
the time. When there is no relationship between what an Another control buzzword is “cascade” and it’s
output controls and something that upsets the process used to identify the use of the output of one controller
a derivative control is almost a necessity. Let’s take our as an input to another. Cascade controls are useful when
ratio totalizer and convert it to a rate controller. It will the output of one process feeds into another. Changes in
look like the diagram in Figure 11-13. With no change in the first process, which are made by the output of one
the process variable the output of the controller is equal controller, create proportional changes in the second
to the output of the reset controller. The rate control oc- process and you can reduce the impact on the control of
curs with changes in the process variable. If the process the second process by using the output of the controller
variable changes slowly it will have very little effect on for the first process as an input for the controller of the
the output because the control air will bleed through second process. Okay, I know it sounds complicated,
the needle valve fast enough that the pressure in the just read it again slowly and you’ll get it. Typically drum
two bellows will remain about the same. If the process level control and furnace pressure control on a boiler
variable changes quickly the air can’t bleed through fast contain cascade control loops.
enough so the difference between what it was and what There are a lot of buzzwords that are specific to an
it is produces an increase or decrease in the output on industry that I don’t have room to describe. You should
top of the reset controller signal. be able to decipher what they mean by looking at the
Some manufacturers called the device a “pre-act- control schematics. A few words on reading schematics
ing” controller because it changed the final output based will be helpful before we get into control processes that
on the action of the process variable. You can see how are specific to boiler plants.
the output of this device would change according to the Control schematics are diagrams on paper that rep-