Page 185 - Boiler plant and distribution system optimization manual
P. 185
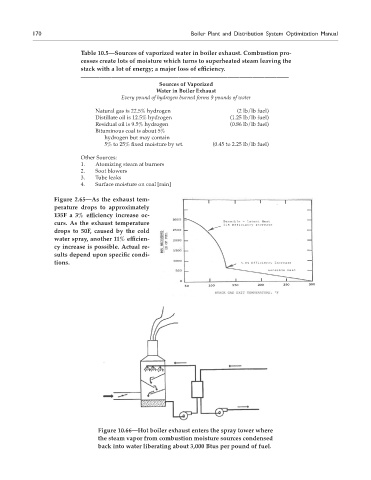
170 Boiler Plant and Distribution System Optimization Manual
Table 10.5—Sources of vaporized water in boiler exhaust. Combustion pro-
cesses create lots of moisture which turns to superheated steam leaving the
stack with a lot of energy; a major loss of efficiency.
——————————————————————————————————
Sources of vaporized
Water in Boiler Exhaust
Every pound of hydrogen burned forms 9 pounds of water
Natural gas is 22.5% hydrogen (2 lb/lb fuel)
Distillate oil is 12.5% hydrogen (1.25 lb/lb fuel)
Residual oil is 9.5% hydrogen (0.86 lb/lb fuel)
Bituminous coal is about 5%
hydrogen but may contain
5% to 25% fixed moisture by wt. (0.45 to 2.25 lb/lb fuel)
Other Sources:
1. Atomizing steam at burners
2. Soot blowers
3. Tube leaks
4. Surface moisture on coal [rain]
Figure 2.65—As the exhaust tem-
perature drops to approximately
135F a 3% efficiency increase oc-
curs. As the exhaust temperature
drops to 50F, caused by the cold
water spray, another 11% efficien-
cy increase is possible. Actual re-
sults depend upon specific condi-
tions.
Figure 10.66—Hot boiler exhaust enters the spray tower where
the steam vapor from combustion moisture sources condensed
back into water liberating about 3,000 Btus per pound of fuel.