Page 189 - Boiler plant and distribution system optimization manual
P. 189
174 Boiler Plant and Distribution System Optimization Manual
over 300°F depending on Boiler pressure and it
contains a lot of energy that can be wasted if it
is not put back to work in the boiler somehow.
About 15% of the blowdown water will flash to
low pressure steam so it is a very good source
of low pressure steam and is usually used in the
deareator/feedwater heater. This steam can be re-
covered in a flash tank and the rest of the heat
contained in the hot water in a heat exchanger. If
steam is not needed, than a simpler heat exchang-
er recovery configuration can be used to just heat
feedwater. (Figure 10.75)
Advantages/Disadvantages
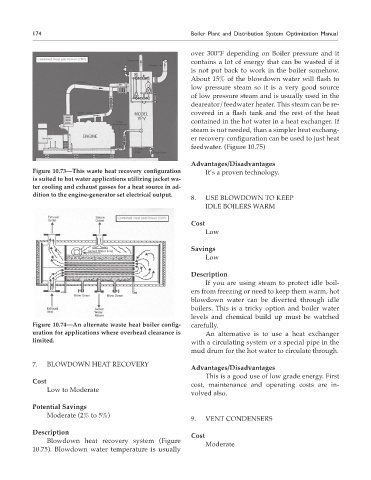
Figure 10.73—This waste heat recovery configuration It’s a proven technology.
is suited to hot water applications utilizing jacket wa-
ter cooling and exhaust gasses for a heat source in ad-
dition to the engine-generator set electrical output.
8. USE BLOWDOWN TO KEEP
IDLE BOILERS WARM
Cost
Low
Savings
Low
Description
If you are using steam to protect idle boil-
ers from freezing or need to keep them warm, hot
blowdown water can be diverted through idle
boilers. This is a tricky option and boiler water
levels and chemical build up must be watched
Figure 10.74—An alternate waste heat boiler config- carefully.
uration for applications where overhead clearance is An alternative is to use a heat exchanger
limited. with a circulating system or a special pipe in the
mud drum for the hot water to circulate through.
7. BLOWDOWN HEAT RECOVERY
Advantages/Disadvantages
This is a good use of low grade energy. First
Cost
cost, maintenance and operating costs are in-
Low to Moderate
volved also.
Potential Savings
Moderate (2% to 5%)
9. VENT CONDENSERS
Description
Cost
Blowdown heat recovery system (Figure
Moderate
10.75). Blowdown water temperature is usually