Page 156 - Cam Design Handbook
P. 156
THB5 8/15/03 1:53 PM Page 144
144 CAM DESIGN HANDBOOK
1500
Deriative of jerk of output motion 0
Spline (k = 10)
Optimized Polydyne
–1500
0 .5 1
Normalized time
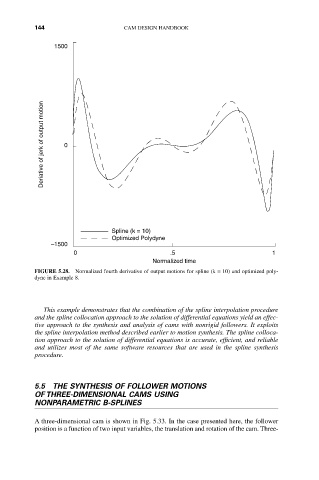
FIGURE 5.28. Normalized fourth derivative of output motions for spline (k = 10) and optimized poly-
dyne in Example 8.
This example demonstrates that the combination of the spline interpolation procedure
and the spline collocation approach to the solution of differential equations yield an effec-
tive approach to the synthesis and analysis of cams with nonrigid followers. It exploits
the spline interpolation method described earlier to motion synthesis. The spline colloca-
tion approach to the solution of differential equations is accurate, efficient, and reliable
and utilizes most of the same software resources that are used in the spline synthesis
procedure.
5.5 THE SYNTHESIS OF FOLLOWER MOTIONS
OF THREE-DIMENSIONAL CAMS USING
NONPARAMETRIC B-SPLINES
A three-dimensional cam is shown in Fig. 5.33. In the case presented here, the follower
position is a function of two input variables, the translation and rotation of the cam. Three-